Neuromechanics of muscle synergies for posture and movement
- PMID: 18304801
- PMCID: PMC4350235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.01.002
Neuromechanics of muscle synergies for posture and movement
Abstract
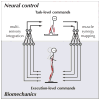
Recent research suggests that the nervous system controls muscles by activating flexible combinations of muscle synergies to produce a wide repertoire of movements. Muscle synergies are like building blocks, defining characteristic patterns of activation across multiple muscles that may be unique to each individual, but perform similar functions. The identification of muscle synergies has strong implications for the organization and structure of the nervous system, providing a mechanism by which task-level motor intentions are translated into detailed, low-level muscle activation patterns. Understanding the complex interplay between neural circuits and biomechanics that give rise to muscle synergies will be crucial to advancing our understanding of neural control mechanisms for movement.
Figures
References
-
- Klein Breteler MD, Simura KJ, Flanders M. Timing of muscle activation in a hand movement sequence. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Tresch MC, Saltiel P, Bizzi E. The construction of movement by the spinal cord. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:162–167. - PubMed
-
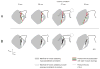
- Torres-Oviedo G, Ting LH. Muscle synergies characterizing human postural responses. J Neurophysiol. 2007 In human postural responses, trial-by-trial variations in muscle activation patterns previously associated with adaptation and habituation were accounted for by variations in muscle synergy activation levels across trials. This suggests that descending cognitive and adaptive influences alter postural strategies through the selection and coordination of muscle synergies. - PubMed
-
- Torres-Oviedo G, Macpherson JM, Ting LH. Muscle synergy organization is robust across a variety of postural perturbations. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96:1530–1546. Muscle synergies for postural control were found to produce consistent endpoint force vectors in a limb-referenced coordinate system. These synergies were robustly used in postural configurations that altered the biomechanical contributions of each muscle synergy to postural stabilization, as well as across different perturbations that dramatically altered sensory information eliciting muscle synergy activation. - PubMed
-
- d’Avella A, Portone A, Fernandez L, Lacquaniti F. Control of Fast-Reaching Movements by Muscle Synergy Combinations. J Neurosci. 2006;26:7791–7810. The authors identify time-varying muscle synergy patterns during reaching movements in humans. They contrast their time-varying muscle synergy formulation with the “static” formulation used by other researchers [2–4] to demonstrate that their formulation may provide a more compact representation in the nervous system. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

