The Salmonella-containing vacuole: moving with the times
- PMID: 18304858
- PMCID: PMC2577838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.01.002
The Salmonella-containing vacuole: moving with the times
Abstract
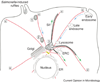
Salmonella pathogenesis is dependent on its ability to invade and replicate within host cells. Following invasion the bacteria remain within a modified phagosome known as the Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV), within which they will survive and replicate. Invasion and SCV biogenesis are dependent on two Type III secretion systems, T3SS1 and T3SS2, which are used to translocate distinct cohorts of bacterial effector proteins into the host cell. Elucidating the roles of individual effector proteins in SCV biogenesis has proven difficult but several distinct themes are now emerging and it is apparent that SCV biogenesis is an extremely dynamic process involving; extensive membrane remodeling, interactions with the endolysosomal pathway, actin rearrangements and microtubule-based movement and tubule extension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic modification of microtubule-dependent transport by effector proteins of intracellular Salmonella enterica.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):897-902. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21803443 Review.
-
Take the tube: remodelling of the endosomal system by intracellular Salmonella enterica.Cell Microbiol. 2015 May;17(5):639-47. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12441. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Cell Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25802001 Review.
-
SopF, a phosphoinositide binding effector, promotes the stability of the nascent Salmonella-containing vacuole.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jul 24;15(7):e1007959. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007959. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31339948 Free PMC article.
-
A glance at Listeria and Salmonella cell invasion: different strategies to promote host actin polymerization.Int J Med Microbiol. 2012 Jan;302(1):19-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Int J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 21783413 Review.
-
Intracellular Salmonella enterica redirect exocytic transport processes in a Salmonella pathogenicity island 2-dependent manner.Traffic. 2006 Jun;7(6):716-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00422.x. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Traffic. 2006. PMID: 16637890
Cited by
-
The bacterial and cellular determinants controlling the recruitment of mTOR to the Salmonella-containing vacuole.Biol Open. 2012 Dec 15;1(12):1215-25. doi: 10.1242/bio.20122840. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Biol Open. 2012. PMID: 23259056 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella acquires lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1) on phagosomes from Golgi via SipC protein-mediated recruitment of host Syntaxin6.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5574-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286120. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22190682 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Knockout Screen in Human Macrophages Identified Host Factors Modulating Salmonella Infection.mBio. 2019 Oct 8;10(5):e02169-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02169-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31594818 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of the vacuole in plant growth and fruit quality.Mol Hortic. 2021 Jun 16;1(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s43897-021-00008-7. Mol Hortic. 2021. PMID: 37789408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ADP-Ribosylating Toxins of Salmonella.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jul 16;11(7):416. doi: 10.3390/toxins11070416. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31315299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

