New benzoyl glucosides and cytotoxic pterosin sesquiterpenes from Pteris ensiformis Burm
- PMID: 18305416
- PMCID: PMC6245482
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules13020255
New benzoyl glucosides and cytotoxic pterosin sesquiterpenes from Pteris ensiformis Burm
Abstract
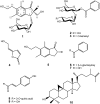
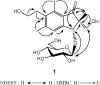
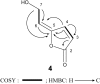
Three new compounds: 2R,3R-pterosin L 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), beta-D-xylopyranosyl(1-->2)-7-O-benzoyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2) and 4-O-benzoyl-beta-D-xylo-pyranosyl(1-->2)-7-O-benzoyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), together with nine known compounds, were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of Pteris ensiformis. 5-[2-Hydroxyethylidene]-2(5H)-furanone (4), which had been synthesized, was isolated from natural sources for the first time. The structures of all isolated compounds were determined on the basis of mass and spectroscopic evidence. Compound 1 and pterosin B (5) show cytotoxicity against HL 60 cells (human leukemia) with the IC(50) values of 3.7 and 8.7 microg/mL, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Gong X.L., Chen Z.H., Liang N.C. Advances in study on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of plants of genus Pteris. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007;32:1382–1387. - PubMed
-
- Jesudass L.L., Manickam V.S., Gopalakrishnan S. Polyphenolic glycosides of Pteris confusa T.G. walker of kothayar hills of the western ghats of south India. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2000;4:77–78.
-
- Salatino M.L., Prado F. Flavonoid glycosides of Pteridaceae from Brazil. J. Bio. System. Eco. 1998;26:761–769. doi: 10.1016/S0305-1978(98)00032-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources