Novel prodrugs for targeting diagnostic and therapeutic radionuclides to solid tumors
- PMID: 18305426
- PMCID: PMC6244955
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules13020391
Novel prodrugs for targeting diagnostic and therapeutic radionuclides to solid tumors
Abstract
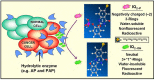
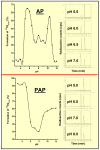
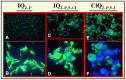
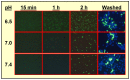
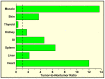
Most cancer therapeutics (chemo, radiation, antibody-based, anti-angiogenic) are at best partially and/or temporarily effective. In general, the causes for failure can be summarized as: (i) poor diffusion and/or nonuniform distribution of drug/prodrug molecules in solid tumors; (ii) high drug concentration and retention in normal tissues (leading to side effects); (iii) requirement for plasma-membrane permeability and/or internalization of drug/prodrug molecules; (iv) low uptake of drug by tumor; (v) lack of retention of drug within tumor (most have gradient-driven reversible binding); and (vi) multidrug resistance. We are developing an innovative technology that aims to surmount these problems by actively concentrating and permanently entrapping radioimaging and radiotherapeutic prodrugs specifically within solid tumors. The approach will enable noninvasive sensing (imaging) and effective therapy of solid tumors, allowing tumor detection, diagnosis, and treatment to be closely coupled (personalized medicine).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural Optimization and Enhanced Prodrug-Mediated Delivery Overcomes Camptothecin Resistance in High-Risk Solid Tumors.Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 1;80(19):4258-4265. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1344. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32839252 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling and experimental evaluation of a novel prodrug for targeting the extracellular space of prostate tumors.Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;67(5):2197-205. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3309. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332350
-
Evaluation of chemical, physical, and biologic properties of tumor-targeting radioiodinated quinazolinone derivative.Bioconjug Chem. 2007 May-Jun;18(3):754-64. doi: 10.1021/bc0602937. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Bioconjug Chem. 2007. PMID: 17385903
-
Antibody-targeted liposomes in cancer therapy and imaging.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008 Feb;5(2):189-204. doi: 10.1517/17425247.5.2.189. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008. PMID: 18248318 Review.
-
Radionuclide cancer therapy.Ann Nucl Med. 1998 Apr;12(2):61-70. doi: 10.1007/BF03164831. Ann Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9637275 Review.
Cited by
-
Tailoring the AIE Chromogen 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole for Use in Enzyme-Triggered Molecular Brachytherapy.Molecules. 2022 Dec 8;27(24):8682. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248682. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kassis A.I., Harapanhalli R.S. Methods for enzyme-mediated tumor diagnosis and therapy. application no. 2001-839779. U.S. Patent Pending. 2001
-
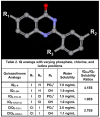
- Chen K., Wang K., Kirichian A.M., Al Aowad A.F., Iyer L.K., Adelstein S.J., Kassis A.I. In silico design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of radioiodinated quinazolinone derivatives for alkaline phosphatase–mediated cancer diagnosis and therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006;5:3001–3013. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0465. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

