Joint estimation of water/fat images and field inhomogeneity map
- PMID: 18306409
- PMCID: PMC3538139
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21522
Joint estimation of water/fat images and field inhomogeneity map
Abstract
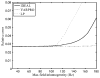
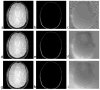
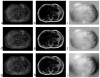
Water/fat separation in the presence of B 0 field inhomogeneity is a problem of considerable practical importance in MRI. This article describes two complementary methods for estimating the water/fat images and the field inhomogeneity map from Dixon-type acquisitions. One is based on variable projection (VARPRO) and the other on linear prediction (LP). The VARPRO method is very robust and can be used in low signal-to-noise ratio conditions because of its ability to achieve the maximum-likelihood solution. The LP method is computationally more efficient, and is shown to perform well under moderate levels of noise and field inhomogeneity. These methods have been extended to handle multicoil acquisitions by jointly solving the estimation problem for all the coils. Both methods are analyzed and compared and results from several experiments are included to demonstrate their performance.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Dixon WT. Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology. 1984;153:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Glover GH, Schneider E. Three-point Dixon technique for true water/fat decomposition with B0 inhomogeneity correction. Magn Reson Med. 1991;18:371–383. - PubMed
-
- Reeder SB, Wen Z, Yu H, Pineda AR, Gold GE, Markl M, Pelc NJ. Multi-coil Dixon chemical species separation with an iterative least squares estimation method. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Reeder SB, Pineda AR, Wen Z, Shimakawa A, Yu H, Brittain JH, Gold GE, Beaulieu CH, Pelc NJ. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): Application with fast spin-echo imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005;54:636–644. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ. Handbook of MRI pulse sequences. Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

