Suppressive effects of a quinoxaline-analogue (Rob 803) on pathogenic immune mechanisms in collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 18307516
- PMCID: PMC2384068
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03613.x
Suppressive effects of a quinoxaline-analogue (Rob 803) on pathogenic immune mechanisms in collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
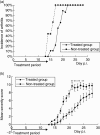
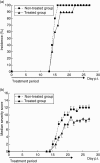
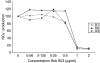
The anti-arthritic effects of the synthetic compound 9-chloro-2,3 dimethyl-6-(N,N-dimetylamino-2-oxoethyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b] quinoxaline (Rob 803) was evaluated by treating Dark Agouti rats with collagen-induced arthritis using three different protocols. Daily subcutaneous treatment with 40 mg/kg/day of Rob 803 from the day of immunization and 14 days forward suppressed arthritis severity significantly and delayed the onset of clinical arthritis. In contrast, similar treatment initiated when individual rats had developed clinical disease (at a score of 2 points) did not suppress disease. Oral treatment with 35 mg/kg/day of Rob 803 from the day of immunization and 21 days forward resulted in a trend towards disease suppression. In vitro analysis of rats treated subcutaneously with Rob 803 revealed an inhibition of T cell proliferation but no effect on the generation of an anti-CII immunoglobulin G response. Further in vitro analysis demonstrated that Rob 803 also inhibited the generation of nitric oxide in macrophages, although at higher concentrations than needed for inhibitory effects on T cell proliferation. Thus we report that early subcutaneous administration of the synthetic substance Rob 803 has anti-rheumatic effects that are probably mediated by affecting the proliferative capacity of lymph node T cells. Rob 803 should be considered as a new candidate substance for anti-rheumatic treatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Longterm protection of mice against collagen-induced arthritis after short-term LF 15-0195 treatment: modulation of B and T lymphocyte activation.J Rheumatol. 2003 May;30(5):918-25. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12734883
-
Immunization with TCR Vbeta10 peptide reduces the frequency of type-II collagen-specific Th1 type T cells in BUB/BnJ (H-2q) mice.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001 Jul-Aug;19(4):385-94. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11491493
-
Inhibitory effects of deer antler aqua-acupuncture, the pilose antler of Cervus Korean TEMMINCK var mantchuricus Swinhoe, on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats.Int Immunopharmacol. 2003 Jul;3(7):1001-10. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5769(03)00098-5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12810357
-
Mucosal tolerance and suppression of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) induced by nasal inhalation of synthetic peptide 184-198 of bovine type II collagen (CII) expressing a dominant T cell epitope.Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Mar;103(3):368-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1996.tb08289.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8608633 Free PMC article.
-
Kirenol exerts a potent anti-arthritic effect in collagen-induced arthritis by modifying the T cells balance.Phytomedicine. 2012 Jul 15;19(10):882-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.04.010. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Phytomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22673798
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of a novel class of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors.Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;81(6):832-45. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.077446. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22434859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong SH, Lord JM. Factors underlying chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2004;52:379–88. - PubMed
-
- Harbecke O, Dahlgren C, Bergman J, Möller L. The synthetic non-toxic drug 2,3-dimethyl-6(2-dimethylaminoethyl)-6H-indolo-(2,3-b)quinoxaline inhibits neutrophil production of reactive oxygen species. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:771–7. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Holmdahl R. Analysis of type II collagen-reactive T cells in the mouse. I. Different regulation of autoreactive vs. non-autoreactive anti-type II collagen T cells in the DBA/1 mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1990;20:1061–6. - PubMed
-
- Smith BD, Martin GR, Miller EJ, Dorfman A, Swarm R. Nature of the collagen synthesized by a transplanted chondrosarcoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975;166:181–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

