MADIBA: a web server toolkit for biological interpretation of Plasmodium and plant gene clusters
- PMID: 18307768
- PMCID: PMC2277412
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-105
MADIBA: a web server toolkit for biological interpretation of Plasmodium and plant gene clusters
Abstract
Background: Microarray technology makes it possible to identify changes in gene expression of an organism, under various conditions. Data mining is thus essential for deducing significant biological information such as the identification of new biological mechanisms or putative drug targets. While many algorithms and software have been developed for analysing gene expression, the extraction of relevant information from experimental data is still a substantial challenge, requiring significant time and skill.
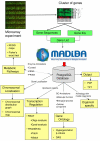
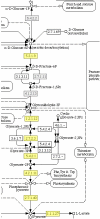
Description: MADIBA (MicroArray Data Interface for Biological Annotation) facilitates the assignment of biological meaning to gene expression clusters by automating the post-processing stage. A relational database has been designed to store the data from gene to pathway for Plasmodium, rice and Arabidopsis. Tools within the web interface allow rapid analyses for the identification of the Gene Ontology terms relevant to each cluster; visualising the metabolic pathways where the genes are implicated, their genomic localisations, putative common transcriptional regulatory elements in the upstream sequences, and an analysis specific to the organism being studied.
Conclusion: MADIBA is an integrated, online tool that will assist researchers in interpreting their results and understand the meaning of the co-expression of a cluster of genes. Functionality of MADIBA was validated by analysing a number of gene clusters from several published experiments - expression profiling of the Plasmodium life cycle, and salt stress treatments of Arabidopsis and rice. In most of the cases, the same conclusions found by the authors were quickly and easily obtained after analysing the gene clusters with MADIBA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PathMAPA: a tool for displaying gene expression and performing statistical tests on metabolic pathways at multiple levels for Arabidopsis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Nov 7;4:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-56. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 14604444 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis Co-expression Tool (ACT): web server tools for microarray-based gene expression analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W504-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl204. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845059 Free PMC article.
-
MILANO--custom annotation of microarray results using automatic literature searches.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 20;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-12. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15661078 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression analysis of metabolic pathways in plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;553:247-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-563-7_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588109 Review.
-
Genome reconstructions of metabolism of Plasmodium RBC and liver stages.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021 Oct;63:259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2021.08.006. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34461385 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptional profiling of three super-hybrid rice combinations.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 3;15(3):3799-815. doi: 10.3390/ijms15033799. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24595241 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq analysis of resistant and susceptible sub-tropical maize lines reveals a role for kauralexins in resistance to grey leaf spot disease, caused by Cercospora zeina.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Nov 13;17(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1137-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29132306 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive epigenome map of Plasmodium falciparum reveals unique mechanisms of transcriptional regulation and identifies H3K36me2 as a global mark of gene suppression.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2015 Sep 17;8:32. doi: 10.1186/s13072-015-0029-1. eCollection 2015. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2015. PMID: 26388940 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum spermidine synthase inhibition results in unique perturbation-specific effects observed on transcript, protein and metabolite levels.BMC Genomics. 2010 Apr 12;11:235. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-235. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20385001 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of drought-responsive signalling network in two contrasting rice cultivars using transcriptome-based approach.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 9;7:42131. doi: 10.1038/srep42131. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28181537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matys V, Fricke E, Geffers R, Gossling E, Haubrock M, Hehl R, Hornischer K, Karas D, Kel AE, Kel-Margoulis OV, Kloos DU, Land S, Lewicki-Potapov B, Michael H, Munch R, Reuter I, Rotert S, Saxel H, Scheer M, Thiele S, Wingender E. TRANSFAC(R): transcriptional regulation, from patterns to profiles. Nucl Acids Res. 2003;31:374–378. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

