Does the association of the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with fasting serum insulin differ by race/ethnicity?
- PMID: 18307789
- PMCID: PMC2292689
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-7-4
Does the association of the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with fasting serum insulin differ by race/ethnicity?
Abstract
Background: The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio has been reported to be as closely correlated with insulin resistance as is the fasting serum insulin concentration (FSI), and therefore it is seen as a clinically useful way to identify the concomitant presence of insulin resistance and dyslipidemia. However, conflicting findings exist for the association of the TG/HDL-C ratio with FSI by race/ethnicity.
Methods: The associations of FSI concentration, serum triglyceride concentrations, and HDL-C were analyzed using log-binomial regression analyses and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis among nondiabetic adults (n = 2652, aged > or = 20 years, 51.2% men) in the United States.
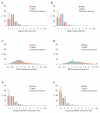
Results: After adjustment for potential confounding effects, the prevalence ratio of hyperinsulinemia was 2.16 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.74 to 2.08) when using a single cutoff point of 3.5, and 2.23 (95% CI, 1.83 to 2.72) when using race/ethnicity-specific cutoff points of 3.0 for non-Hispanic whites and Mexican Americans and 2.0 for non-Hispanic blacks for the TG/HDL-C ratio. The area under the ROC curve of the TG/HDL-C ratio for predicting hyperinsulinemia was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.74 to 0.79), 0.75 (95% CI, 0.69 to 0.77), and 0.74 (95% CI, 0.69 to 0.76) for non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic blacks, and Mexican Americans, respectively.
Conclusion: There was a significant association between the TG/HDL-C ratio and FSI among three major racial/ethnic groups in the United States. Our results add further support to the notion that the TG/HDL-C ratio may be a clinically simple and useful indicator for hyperinsulinemia among nondiabetic adults regardless of race/ethnicity.
Figures

References
-
- Ferrannini E, Natali A, Capaldo B, Lehtovirta M, Jacob S, Yki-Jarvinen H. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and blood pressure: role of age and obesity. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR) Hypertension. 1997;30:1144–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

