GPs' classification of headache: is primary headache underdiagnosed?
- PMID: 18307854
- PMCID: PMC2233960
- DOI: 10.3399/bjgp08X264072
GPs' classification of headache: is primary headache underdiagnosed?
Abstract
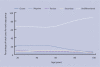
With a high economic, social, and personal burden, headache remains an important health problem. How UK GPs diagnose headache in the UK is unknown. In this study, a large primary care database was used and diagnostic categories were described for 91121 adult patients with new-onset headache, that is, patients who had not consulted for headache in the previous year. Seventy per cent of headaches were not given a diagnostic label, 24% were diagnosed as primary, and 6% as secondary headaches. It is suggested that GPs' difficulty in diagnosing headache presentations contributes to the high level of morbidity and unmet need in this disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
Easing the pain: challenges and opportunities in headache management.Br J Gen Pract. 2008 Feb;58(547):77-8. doi: 10.3399/bjgp08X264009. Br J Gen Pract. 2008. PMID: 18307847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of headache.Br J Gen Pract. 2008 Apr;58(549):282-3. doi: 10.3399/bjgp08X279904. Br J Gen Pract. 2008. PMID: 18387240 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Headache management in general practice.Br J Gen Pract. 2008 Apr;58(549):283. doi: 10.3399/bjgp08X279913. Br J Gen Pract. 2008. PMID: 18387245 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Steiner T, Scher A, Stewart F, et al. The prevalence and disability burden of adult migraine in England and their relationships to age, gender and ethnicity. Cephalalgia. 2003;23(7):519–527. - PubMed
-
- Solomon G, Skobierand F, Gragg L. Quality of life and well-being of headache patients: measurement by the medical outcomes study instrument. Headache. 1993;33(7):351–358. - PubMed
-
- Terwindt G, Ferrari M, Tijhus M, et al. The impact of migraine on quality of life in the general population — The GEM Study. Neurology. 2000;55(5):624–629. - PubMed
-
- Dowson A, Jagger S. The UK migraine patient survey: quality of life and treatment. Curr Med Res Opin. 1999;15(4):241–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical