Imaging and dosimetry of 99mTc EC annexin V: preliminary clinical study targeting apoptosis in breast tumors
- PMID: 18308577
- PMCID: PMC2562036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.01.012
Imaging and dosimetry of 99mTc EC annexin V: preliminary clinical study targeting apoptosis in breast tumors
Abstract
Background: Early detection of cellular events is important to predict the outcome of the patients. This study was aimed to use (99m)Tc EC-annexin V to image tumor cells undergoing apoptosis.
Methods: In 10 patients with breast cancer, scintigraphic images and dosimetric estimates were obtained after administering (99m)Tc EC-annexin V.
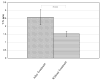
Results: Nine of the 10 cases showed detectable (99m)Tc EC-annexin V uptake in tumor. Higher values of T/N ratios are associated with patient after treatment.
Conclusions: Apoptosis can be quantified using (99m)Tc EC-annexin V.
Figures




References
-
- Buchholz TA, Hunt KK, Whitman GJ, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast carcinoma: multidisciplinary considerations of benefits and risks. Cancer. 2003;98(6):1150–60. - PubMed
-
- Cole BF, Gelber RD, Gelber S, et al. Polychemotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised clinical trials with quality-adjusted survival analysis. The Lancet. 2001;358(9278):277–86. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(8):2672–2685. - PubMed
-
- Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, et al. The effect on tumor response of adding sequential preoperative docetaxel to preoperative doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: preliminary results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(22):4165–74. - PubMed
-
- Green MC, Buzdar AU, Smith T, et al. Weekly Paclitaxel Improves Pathologic Complete Remission in Operable Breast Cancer When Compared With Paclitaxel Once Every 3 Weeks. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(25):5983–5992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

