Chronic inhibition of GABA synthesis in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis elicits anxiety-like behavior
- PMID: 18308797
- PMCID: PMC3065212
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881107082902
Chronic inhibition of GABA synthesis in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis elicits anxiety-like behavior
Abstract
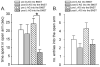
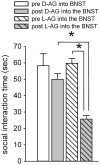
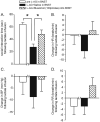
The current study tested the hypothesis that chronic loss of inhibitory GABAergic tone in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), a region implicated in anxiety behavior, results in generalized anxiety disorder-like behaviors without panic-like responses (i.e., tachycardia, hypertension and tachypnea) following panicogenic stimuli (e.g., sodium lactate infusions). To test this hypothesis, the GABA synthesis inhibitor L-allylglycine (L-AG) or its inactive isomer D-AG was chronically infused into the BNST of male rats via osmotic mini-pumps. L-AG, but not D-AG, treated rats had increased anxiety-like behavior as measured by social interaction (SI) and elevated-plus maze paradigms. Restoring GABAergic tone, with 100pmoles/100nl of muscimol (a GABA(A) receptor agonist), in the BNST of L-AG treated rats attenuated L-AG-induced anxiety-like behavior in the SI test. To assess panic-like states, L-AG treated rats were intravenously infused with 0.5 M sodium lactate, a panicogenic agent, prior to assessing SI and cardiorespiratory responses. L-AG decreased SI duration again; however, sodium lactate did not induce panic-like cardiorespiratory responses. These findings demonstrate that GABA inhibition in the BNST elicits anxiety-like behavior without increasing sensitivity to lactate, thus suggesting a behavioral profile similar to that of generalized anxiety-like behavior rather than that of panic.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dorsomedial hypothalamic GABA dysfunction produces physiological arousal following sodium lactate infusions.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996 Oct;55(2):249-56. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(96)00077-9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996. PMID: 8951961
-
Panic-prone state induced in rats with GABA dysfunction in the dorsomedial hypothalamus is mediated by NMDA receptors.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 28;26(26):7093-104. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0408-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16807338 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated stimulation of CRF receptors in the BNST of rats selectively induces social but not panic-like anxiety.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Oct;33(11):2586-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301674. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18288095 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) expression and signaling in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) in mediating the behavioral consequences of chronic stress.J Mol Neurosci. 2010 Nov;42(3):327-40. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9364-7. Epub 2010 Apr 20. J Mol Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20405238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoarchitecture of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: Neurophenotypic diversity and function.Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;179:385-402. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819975-6.00025-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34225977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Threat imminence dictates the role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in contextual fear.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020 Jan;167:107116. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.107116. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 31740383 Free PMC article.
-
VGluT3 BNST neurons transmit GABA and restrict feeding without affecting rewarding or aversive processing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 2:2025.01.01.631003. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.01.631003. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Mol Metab. 2025 Aug;98:102178. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102178. PMID: 39803518 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cell-type specific deletion of GABA(A)α1 in corticotropin-releasing factor-containing neurons enhances anxiety and disrupts fear extinction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 2;109(40):16330-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119261109. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22992651 Free PMC article.
-
Is it all in the family? The effects of early social structure on neural-behavioral systems of prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster).Neuroscience. 2012 Aug 2;216:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.063. Epub 2012 May 1. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22561732 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced dendritic availability of μ-opioid receptors in inhibitory neurons of the extended amygdala in mice deficient in the corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptor.Synapse. 2011 Jan;65(1):8-20. doi: 10.1002/syn.20810. Synapse. 2011. PMID: 20506149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alheid GF, Beltramino CA, De Olmos JS, Forbes MS, Swanson DJ, Heimer L. The neuronal organization of the supracapsular part of the stria terminalis in the rat: the dorsal component of the extended amygdala. Neuroscience. 1998;84:967–996. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–557. - PubMed
-
- Bali B, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Kovacs KJ. Visualization of stress-responsive inhibitory circuits in the GAD65-eGFP transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett. 2005;380:60–65. - PubMed
-
- bEgli RE, Winder DG. Dorsal and ventral distribution of excitable and synaptic properties of neurons of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurophysiol. 2003;90:405–414. - PubMed
-
- Carr DB, Sheehan DV, Surman OS, Coleman JH, Greenblatt DJ, Heninger GR, Jones KJ, Levine PH, Watkins WD. Neuroendocrine correlates of lactate-induced anxiety and their response to chronic alprazolam therapy. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143:483–494. - PubMed

