Synaptotagmin-1 and -7 are functionally overlapping Ca2+ sensors for exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells
- PMID: 18308932
- PMCID: PMC2268838
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0712373105
Synaptotagmin-1 and -7 are functionally overlapping Ca2+ sensors for exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells
Abstract
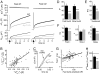
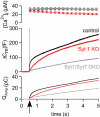
Synaptotagmin-1, the canonical isoform of the synaptotagmin family, is a Ca(2+) sensor for fast synchronous neurotransmitter release in forebrain neurons and chromaffin cells. Even though deletion of synaptotagmin-1 abolishes fast exocytosis in chromaffin cells, it reduces overall secretion by only 20% because of the persistence of slow exocytosis. Therefore, another Ca(2+) sensor dominates release in these cells. Synaptotagmin-7 has a higher Ca(2+) affinity and slower binding kinetics than synaptotagmin-1, matching the proposed properties for the second, slower Ca(2+) sensor. Here, we examined Ca(2+)-triggered exocytosis in chromaffin cells from KO mice lacking synaptotagmin-7, and from knockin mice containing normal levels of a mutant synaptotagmin-7 whose C(2)B domain does not bind Ca(2+). In both types of mutant chromaffin cells, Ca(2+)-triggered exocytosis was decreased dramatically. Moreover, in chromaffin cells lacking both synaptotagmin-1 and -7, only a very slow release component, accounting for approximately 30% of WT exocytosis, persisted. These data establish synaptotagmin-7 as a major Ca(2+) sensor for exocytosis in chromaffin cells, which, together with synaptotagmin-1, mediates almost all of the Ca(2+) triggering of exocytosis in these cells, a surprising result, considering the lack of a role of synaptotagmin-7 in synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

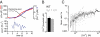

Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of synaptotagmin-7 function in synaptic vesicle exocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 11;105(10):3986-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712372105. Epub 2008 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18308933 Free PMC article.
-
Push-and-pull regulation of the fusion pore by synaptotagmin-7.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 2;107(44):19032-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014070107. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20956309 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric stabilization of calcium and phosphoinositide dual binding engages several synaptotagmins in fast exocytosis.Elife. 2022 Aug 5;11:e74810. doi: 10.7554/eLife.74810. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35929728 Free PMC article.
-
CaV1.3 as pacemaker channels in adrenal chromaffin cells: specific role on exo- and endocytosis?Channels (Austin). 2010 Nov-Dec;4(6):440-6. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.6.12866. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 21084859 Review.
-
C2-domain containing calcium sensors in neuroendocrine secretion.J Neurochem. 2016 Dec;139(6):943-958. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13865. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27731902 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuromodulator release in neurons requires two functionally redundant calcium sensors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 4;118(18):e2012137118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012137118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33903230 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine is critical for vesicle fission during clathrin-mediated endocytosis.J Neurochem. 2020 Jan;152(1):48-60. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14886. Epub 2019 Oct 27. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 31587282 Free PMC article.
-
Role of calcium and EPAC in norepinephrine-induced ghrelin secretion.Endocrinology. 2014 Jan;155(1):98-107. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1691. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24189139 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-7 as a positive regulator of glucose-induced glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in mice.Diabetologia. 2011 Jul;54(7):1824-30. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2119-3. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21424898
-
Molecular Mechanisms for the Coupling of Endocytosis to Exocytosis in Neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Mar 13;10:47. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00047. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28348516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maximov A, Südhof TC. Autonomous function of synaptotagmin 1 in triggering asynchronous release independent of asynchronous release. Neuron. 2005;48:547–554. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Chacon R, et al. Synaptotagmin I functions as a calcium regulator of release probability. Nature. 2001;410:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M, et al. Synaptotagmin I: A major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell. 1994;79:717–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

