Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family
- PMID: 18308936
- PMCID: PMC2268826
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0712321105
Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family
Abstract
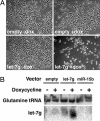
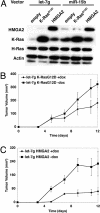
Many microRNAs (miRNAs) target mRNAs involved in processes aberrant in tumorigenesis, such as proliferation, survival, and differentiation. In particular, the let-7 miRNA family has been proposed to function in tumor suppression, because reduced expression of let-7 family members is common in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, we show that let-7 functionally inhibits non-small cell tumor development. Ectopic expression of let-7g in K-Ras(G12D)-expressing murine lung cancer cells induced both cell cycle arrest and cell death. In tumor xenografts, we observed significant growth reduction of both murine and human non-small cell lung tumors when overexpression of let-7g was induced from lentiviral vectors. In let-7g expressing tumors, reductions in Ras family and HMGA2 protein levels were detected. Importantly, let-7g-mediated tumor suppression was more potent in lung cancer cell lines harboring oncogenic K-Ras mutations than in lines with other mutations. Ectopic expression of K-Ras(G12D) largely rescued let-7g mediated tumor suppression, whereas ectopic expression of HMGA2 was less effective. Finally, in an autochthonous model of NSCLC in the mouse, let-7g expression substantially reduced lung tumor burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
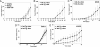

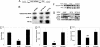
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–524. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115:787–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

