TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 18309045
- PMCID: PMC7116650
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1154584
TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
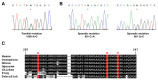
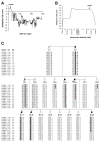
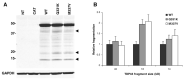
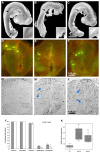
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal motor neuron disorder characterized pathologically by ubiquitinated TAR DNA binding protein (TDP-43) inclusions. The function of TDP-43 in the nervous system is uncertain, and a mechanistic role in neurodegeneration remains speculative. We identified neighboring mutations in a highly conserved region of TARDBP in sporadic and familial ALS cases. TARDBPM337V segregated with disease within one kindred and a genome-wide scan confirmed that linkage was restricted to chromosome 1p36, which contains the TARDBP locus. Mutant forms of TDP-43 fragmented in vitro more readily than wild type and, in vivo, caused neural apoptosis and developmental delay in the chick embryo. Our evidence suggests a pathophysiological link between TDP-43 and ALS.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

