Hybrid neurons in a microRNA mutant are putative evolutionary intermediates in insect CO2 sensory systems
- PMID: 18309086
- PMCID: PMC2714168
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1149483
Hybrid neurons in a microRNA mutant are putative evolutionary intermediates in insect CO2 sensory systems
Abstract
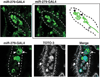
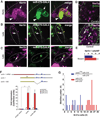
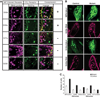
Carbon dioxide (CO2) elicits different olfactory behaviors across species. In Drosophila, neurons that detect CO2 are located in the antenna, form connections in a ventral glomerulus in the antennal lobe, and mediate avoidance. By contrast, in the mosquito these neurons are in the maxillary palps (MPs), connect to medial sites, and promote attraction. We found in Drosophila that loss of a microRNA, miR-279, leads to formation of CO2 neurons in the MPs. miR-279 acts through down-regulation of the transcription factor Nerfin-1. The ectopic neurons are hybrid cells. They express CO2 receptors and form connections characteristic of CO2 neurons, while exhibiting wiring and receptor characteristics of MP olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). We propose that this hybrid ORN reveals a cellular intermediate in the evolution of species-specific behaviors elicited by CO2.
Figures

References
-
- Kellogg FE. J. Insect Physiol. 1970;16:99. [CrossRef] [ISI] [Medline][UC-eLinks] - PubMed
-
- Grant AJ, O′Connell RJ. Ciba Found. Symp. 1996;200:233. [Medline][UC-eLinks] - PubMed
-
- Bogner F. Physiol. Entomol. 1992;17:1992. [UC-eLinks]
-
- Thom C, Guerenstein PG, Mechaber WL, Hildebrand JG. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004;30:1285. [CrossRef] [ISI] [Medline][UC-eLinks] - PubMed
-
- Bogner F, Boppre M, Ernst KD, Boeckh J. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1986;158:741. [CrossRef] [Medline][UC-eLinks] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

