Plx1 is required for chromosomal DNA replication under stressful conditions
- PMID: 18309293
- PMCID: PMC2265110
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.29
Plx1 is required for chromosomal DNA replication under stressful conditions
Abstract
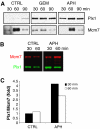
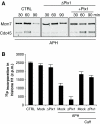
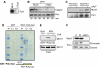
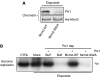
Polo-like kinase (Plk)1 is required for mitosis progression. However, although Plk1 is expressed throughout the cell cycle, its function during S-phase is unknown. Using Xenopus laevis egg extracts, we demonstrate that Plx1, the Xenopus orthologue of Plk1, is required for DNA replication in the presence of stalled replication forks induced by aphidicolin, etoposide or reduced levels of DNA-bound Mcm complexes. Plx1 binds to chromatin and suppresses the ATM/ATR-dependent intra-S-phase checkpoint that inhibits origin firing. This allows Cdc45 loading and derepression of DNA replication initiation. Checkpoint activation increases Plx1 binding to the Mcm complex through its Polo box domain. Plx1 recruitment to chromatin is independent of checkpoint mediators Tipin and Claspin. Instead, ATR-dependent phosphorylation of serine 92 of Mcm2 is required for the recruitment of Plx1 to chromatin and for the recovery of DNA replication under stress. Depletion of Plx1 leads to accumulation of chromosomal breakage that is prevented by the addition of recombinant Plx1. These data suggest that Plx1 promotes genome stability by regulating DNA replication under stressful conditions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adaptation of a DNA replication checkpoint response depends upon inactivation of Claspin by the Polo-like kinase.Cell. 2004 May 28;117(5):575-88. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00417-9. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15163406
-
Mcm2 is a direct substrate of ATM and ATR during DNA damage and DNA replication checkpoint responses.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 17;279(51):53353-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408026200. Epub 2004 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15448142
-
Separation of intra-S checkpoint protein contributions to DNA replication fork protection and genomic stability in normal human fibroblasts.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 15;12(2):332-45. doi: 10.4161/cc.23177. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23255133 Free PMC article.
-
Xenopus Polo-like kinase Plx1: a multifunctional mitotic kinase.Oncogene. 2005 Jan 10;24(2):238-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208220. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15640839 Review.
-
Claspin: timing the cell cycle arrest when the genome is damaged.Cell Cycle. 2006 Dec;5(24):2831-4. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.24.3559. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17172868 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of rictor as a novel substrate of Polo-like kinase 1.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(5):755-60. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2014.998050. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25714006 Free PMC article.
-
A TRilogy of ATR's Non-Canonical Roles Throughout the Cell Cycle and Its Relation to Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;16(20):3536. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203536. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage Response in Xenopus laevis Cell-Free Extracts.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2267:103-144. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1217-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33786788 Free PMC article.
-
Replication checkpoint: tuning and coordination of replication forks in s phase.Genes (Basel). 2013 Aug 19;4(3):388-434. doi: 10.3390/genes4030388. Genes (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24705211 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 depletion induces DNA damage in early S prior to caspase activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(10):2609-21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01277-08. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19289504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahr A, Holtrich U, Solbach C, Scharl A, Strebhardt K, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2001) Molecular classification of breast cancer patients by gene expression profiling. J Pathol 195: 312–320 - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Kovar J, Sissons S, Cox K, Matter W, Chadwell F, Luan P, Vlahos CJ, Schutz-Geschwender A, Olive DM (2005) A cell-based immunocytochemical assay for monitoring kinase signaling pathways and drug efficacy. Anal Biochem 338: 136–142 - PubMed
-
- Costanzo V, Gautier J (2003) Single-strand DNA gaps trigger an ATR- and Cdc7-dependent checkpoint. Cell Cycle 2: 17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

