Microfluidics of cytoplasmic streaming and its implications for intracellular transport
- PMID: 18310326
- PMCID: PMC2268784
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707223105
Microfluidics of cytoplasmic streaming and its implications for intracellular transport
Abstract
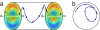
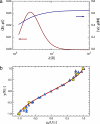
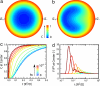
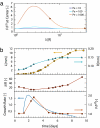
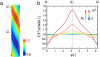
Found in many large eukaryotic cells, particularly in plants, cytoplasmic streaming is the circulation of their contents driven by fluid entrainment from particles carried by molecular motors at the cell periphery. In the more than two centuries since its discovery, streaming has frequently been conjectured to aid in transport and mixing of molecular species in the cytoplasm and, by implication, in cellular homeostasis, yet no theoretical analysis has been presented to quantify these processes. We show by a solution to the coupled dynamics of fluid flow and diffusion appropriate to the archetypal "rotational streaming" of algal species such as Chara and Nitella that internal mixing and the transient dynamical response to changing external conditions can indeed be enhanced by streaming, but to an extent that depends strongly on the pitch of the helical flow. The possibility that this may have a developmental consequence is illustrated by the coincidence of the exponential growth phase of Nitella and the point of maximum enhancement of those processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Corti B. Osservazione Microscopische sulla Tremella e sulla Circulazione del Fluido in Una Planto Acquaguola. Lucca, Italy: Appresso Giuseppe Rocchi; 1774.
-
- Pickard WF. Plant Cell Environ. 2003;26:1–15.
-
- Allen RD, Allen NS. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:469–495. - PubMed
-
- Shimmen T. J Plant Res. 2007;120:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Allen NS, Allen RD. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:497–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

