Chlamydia pneumoniae GroEL1 protein is cell surface associated and required for infection of HEp-2 cells
- PMID: 18310329
- PMCID: PMC2394982
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01638-07
Chlamydia pneumoniae GroEL1 protein is cell surface associated and required for infection of HEp-2 cells
Abstract
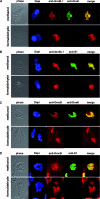
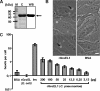
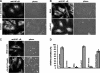
Chlamydia pneumoniae is an important obligate intracellular pathogen that replicates within an inclusion in the eukaryotic cell. The initial event of a chlamydial infection is the adherence to and subsequent uptake of the infectious elementary bodies (EBs) by the human cell. These processes require yet-unidentified bacterial and eukaryotic surface proteins. The GroEL1 protein, which exhibits a very strong antigenicity and in vitro can activate various eukaryotic cells, is a potential pathogenicity factor. We localized the protein during the infection process and found it in the inclusion but outside the chlamydial particles. GroEL1 was also localized on the surface of EBs, and the protein could be washed off the EBs. Latex beads coated with recombinantly produced GroEL1 (rGroEL1) bound in a dose-dependent manner to HEp-2 cells. Likewise, GroEL1, when expressed and displayed on the yeast cell surface, mediated adhesion to HEp-2 cells. Interestingly, the homologous GroEL2 and GroEL3 proteins showed no adhesive properties. Incubation of primary umbilical vein endothelial cells with soluble GroEL1 and GroEL1-coated latex beads activated the translocation of the general transcription factor NF-kappaB into the nucleus. Finally, preincubation of HEp-2 cells with rGroEL1 significantly reduced subsequent infection with C. pneumoniae, although adhesion of infectious bacteria to eukaryotic cells was not affected. Taken together, these data support a role for extracellular GroEL1 in the establishment of the chlamydial infection.
Figures
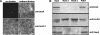



Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of the multiple GroEL proteins of Chlamydiae.J Bacteriol. 2003 Mar;185(6):1958-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.6.1958-1966.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12618460 Free PMC article.
-
GroEL1, a heat shock protein 60 of Chlamydia pneumoniae, impairs neovascularization by decreasing endothelial progenitor cell function.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 23;8(12):e84731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084731. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376840 Free PMC article.
-
GroEL1, from Chlamydia pneumoniae, induces vascular adhesion molecule 1 expression by p37(AUF1) in endothelial cells and hypercholesterolemic rabbit.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042808. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22900050 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydial persistence: beyond the biphasic paradigm.Infect Immun. 2004 Apr;72(4):1843-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.1843-1855.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15039303 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Chlamydophila pneumoniae. Mechanisms of target cell infection and activation.Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;94(2):319-26. doi: 10.1160/TH05-04-0261. Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 16113821 Review.
Cited by
-
Lineage structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae may be driven by immune selection on the groEL heat-shock protein.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08990-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831154 Free PMC article.
-
Essential domains of Anaplasma phagocytophilum invasins utilized to infect mammalian host cells.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Feb 6;11(2):e1004669. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004669. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25658707 Free PMC article.
-
The Chlamydia pneumoniae invasin protein Pmp21 recruits the EGF receptor for host cell entry.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003325. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003325. Epub 2013 Apr 25. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23633955 Free PMC article.
-
Direct targeting of host microtubule and actin cytoskeletons by a chlamydial pathogenic effector protein.J Cell Sci. 2024 Sep 1;137(17):jcs263450. doi: 10.1242/jcs.263450. Epub 2024 Sep 6. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 39099397 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of two ancestral chaperone systems into one: the evolution of eukaryotic molecular chaperones in light of eukaryogenesis.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 Feb;31(2):410-8. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst212. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24188869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bavoil, P., R. S. Stephens, and S. Falkow. 1990. A soluble 60 kilodalton antigen of Chlamydia spp. is a homologue of Escherichia coli GroEL. Mol. Microbiol. 4461-469. - PubMed
-
- Bergonzelli, G. E., D. Granato, R. D. Pridmore, L. F. Marvin-Guy, D. Donnicola, and I. E. Corthesy-Theulaz. 2006. GroEL of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 (NCC 533) is cell surface associated: potential role in interactions with the host and the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 74425-434. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

