Performance of AAV8 vectors expressing human factor IX from a hepatic-selective promoter following intravenous injection into rats
- PMID: 18312698
- PMCID: PMC2267784
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-0556-6-9
Performance of AAV8 vectors expressing human factor IX from a hepatic-selective promoter following intravenous injection into rats
Abstract
Background: Vectors based on adeno-associated virus-8 (AAV8) have shown efficiency and efficacy for liver-directed gene therapy protocols following intravascular injection, particularly in relation to haemophilia gene therapy. AAV8 has also been proposed for gene therapy targeted at skeletal and cardiac muscle, again via intravascular injection. It is important to assess vector targeting at the level of virion accumulation and transgene expression in multiple species to ascertain potential issues relating to species variation in infectivity profiles.
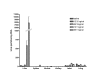
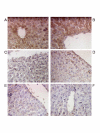
Methods: We used AAV8 vectors expressing human factor IX (FIX) from the liver-specific LP-1 promoter and administered this virus via the intravascular route of injection into 12 week old Wistar Kyoto rats. We assessed FIX levels in serum by ELISA and transgene expression at sacrifice by immunohistochemistry using anti-FIX antibodies. Vector DNA levels in organs we determined by real time PCR.
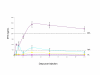
Results: Administration of 1 x 10(11) or 5 x 10(11) scAAV8-LP1-hFIX vector particles/rat resulted in efficient production of physiological hFIX levels, respectively in blood assessed 4 weeks post-injection. This was maintained for the 4 month duration of the study. At 4 months we observed liver persistence of vector with minimal non-hepatic distribution.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that AAV8 is a robust vector for delivering therapeutic genes into rat liver following intravascular injection.
Figures
References
-
- Snyder RO, Miao C, Meuse L, Tubb J, Donahue AR, Lin HF, Stafford DW, Patel S, Thompson AR, Nichols T, Read MS, Bellinger DA, Brinkhous KM, Kay MA. Correction of hemonphilia B in canine and murine models using recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Nature medicine. 1999;5:64–70. doi: 10.1038/13518. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Snyder RO, Miao CH, Patijn GA, Spratt SK, Danos O, Nagy D, Gown AM, Winther B, Meuse L, Cohen LK, Thompson AR, Kay MA. Persistent and therapeutic concentrations of human factor IX in mice after hepatic gene transfer of recombinant AAV vectors. Nature genetics. 1997;16:270–276. doi: 10.1038/ng0797-270. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mount JD, Herzog RW, Tillson DM, Goodman SA, Robinson N, McCleland ML, Bellinger D, Nichols TC, Arruda VR, Lothrop CD, High KA. Sustained phenotypic correction of hemophilia B dogs with a factor IX null mutation by liver-directed gene therapy. Blood. 2002;99:2670–2676. doi: 10.1182/blood.V99.8.2670. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nathwani AC, Davidoff AM, Hanawa H, Hu Y, Hoffer FA, Nikanorov A, Slaughter C, Ng SYC, Junfang Z, Lozier JN, Mandrell TD, Vanin EF, Nienhuis AW. Sustained high-level expression of human factor IX (Hfix) after liver-targeted delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus encoding the Hfix gene in rhesus macaques. Gene therapy. 2002;100:1662–1669. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

