Tolerance to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in rats exposed to single high-dose binges
- PMID: 18313226
- PMCID: PMC2390896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.007
Tolerance to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in rats exposed to single high-dose binges
Abstract
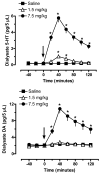
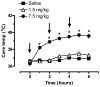
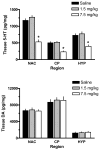
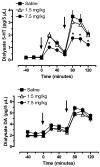
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA or ecstasy) stimulates the transporter-mediated release of monoamines, including 5-HT. High-dose exposure to MDMA causes persistent 5-HT deficits (e.g. depletion of brain 5-HT) in animals, yet the functional and clinical relevance of such deficits are poorly defined. Here we examine functional consequences of MDMA-induced 5-HT depletions in rats. Male rats received binges of three i.p. injections of MDMA or saline, one injection every 2 h; MDMA was given at a threshold pharmacological dose (1.5 mg/kgx3, low dose) or at a fivefold higher amount (7.5 mg/kgx3, high dose). One week later, jugular catheters and intracerebral guide cannulae were implanted. Two weeks after binges, rats received acute i.v. challenge injections of 1 and 3 mg/kg MDMA. Neuroendocrine effects evoked by i.v. MDMA (prolactin and corticosterone secretion) were assessed via serial blood sampling, while neurochemical effects (5-HT and dopamine release) were assessed via microdialysis in brain. MDMA binges elevated core temperatures only in the high-dose group, with these same rats exhibiting approximately 50% loss of forebrain 5-HT 2 weeks later. Prior exposure to MDMA did not alter baseline plasma hormones or dialysate monoamines, and effects of i.v. MDMA were similar in saline and low-dose groups. By contrast, rats pretreated with high-dose MDMA displayed significant reductions in evoked hormone secretion and 5-HT release when challenged with i.v. MDMA. As tolerance developed only in rats exposed to high-dose binges, hyperthermia and 5-HT depletion are implicated in this phenomenon. Our results suggest that MDMA tolerance in humans may reflect 5-HT deficits which could contribute to further dose escalation.
Figures




References
-
- Ball KT, Budreau D, Rebec GV. Acute effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on striatal single-unit activity and behavior in freely moving rats: differential involvement of dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors. Brain Res. 2003;994:203–215. - PubMed
-
- Bankson MG, Cunningham KA. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) as a unique model of serotonin receptor function and serotonin-dopamine interactions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:846–852. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Yeh SY, O’Hearn E, Molliver ME, Kuhar MJ, De Souza EB. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine destroy serotonin terminals in rat brain: quantification of neurodegeneration by measurement of [3H]paroxetine-labeled serotonin uptake sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;242:911–916. - PubMed
-
- Baumann MH, Clark RD, Budzynski AG, Partilla JS, Blough BE, Rothman RB. N-substituted piperazines abused by humans mimic the molecular mechanism of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or ‘Ecstasy’) Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:550–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

