Mitochondrial protein thiol modifications in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: effect on HMG-CoA synthase
- PMID: 18313239
- PMCID: PMC2377066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.01.010
Mitochondrial protein thiol modifications in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: effect on HMG-CoA synthase
Abstract
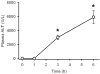
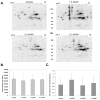
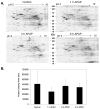
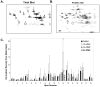
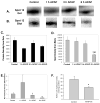
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is the leading cause of drug related liver failure in many countries. N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a reactive metabolite that is formed by the metabolism of APAP. NAPQI preferentially binds to glutathione and then cellular proteins. NAPQI binding is considered an upstream event in the pathophysiology, especially when binding to mitochondrial proteins and therefore leads to mitochondrial toxicity. APAP caused a significant increase in liver toxicity 3h post-APAP administration as measured by increased serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. Using high-resolution mitochondrial proteomics techniques to measure thiol and protein changes, no significant change in global thiol levels was observed. However, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase 2 (HMG-CoA synthase) had significantly decreased levels of reduced thiols and activity after APAP treatment. HMG-CoA synthase is a key regulatory enzyme in ketogenesis and possesses a number of critical cysteines in the active site. Similarly, catalase, a key enzyme in hydrogen peroxide metabolism, also showed modification in protein thiol content. These data indicate post-translational modifications of a few selected proteins involved in mitochondrial and cellular regulation of metabolism during liver toxicity after APAP overdose. The pathophysiological relevance of these limited changes in protein thiols remains to be investigated.
Figures
References
-
- Bailey SM, Landar A, Darley-Usmar V. Mitochondrial proteomics in free radical research. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38:175–188. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Knight TR, Farhood A, Jaeschke H. Scavenging peroxynitrite with glutathione promotes regeneration and enhances survival during acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J Pharmacol Exper Therap. 2003;307:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Cover C, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H. Nuclear translocation of endonuclease G and apoptosis-inducing factor during acetaminophen-induced liver cell injury. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94:217–225. - PubMed
-
- Barford D. The role of cysteine residues as redox-sensitive regulatory switches. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:679–686. - PubMed
-
- Beer SM, Taylor ER, Brown SE, Dahm CC, Costa NJ, Runswick MJ, Murphy MP. Glutaredoxin 2 catalyzes the reversible oxidation and glutathionylation of mitochondrial membrane thiol proteins. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47939–47951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

