Alpha-synuclein aggregation alters tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation and immunoreactivity: lessons from viral transduction of knockout mice
- PMID: 18314273
- PMCID: PMC2440662
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.02.014
Alpha-synuclein aggregation alters tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation and immunoreactivity: lessons from viral transduction of knockout mice
Abstract
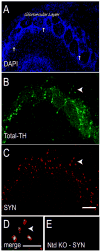
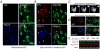
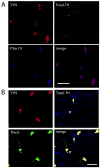
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate limiting enzyme in catecholamine synthesis, is frequently used as a marker of dopaminergic neuronal loss in animal models of Parkinson's disease (PD). We have been exploring the normal function of the PD-related protein alpha-synuclein (alpha-Syn) with regard to dopamine synthesis. TH is activated by the phosphorylation of key seryl residues in the TH regulatory domain. Using in vitro models, our laboratory discovered that alpha-Syn inhibits TH by acting to reduce TH phosphorylation, which then reduces dopamine synthesis [X.-M. Peng, R. Tehranian, P. Dietrich, L. Stefanis, R.G. Perez, Alpha-synuclein activation of protein phosphatase 2A reduces tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in dopaminergic cells, J. Cell. Sci. 118 (2005) 3523-3530; R.G. Perez, J.C. Waymire, E. Lin, J.J. Liu, F. Guo, M.J. Zigmond, A role for alpha-synuclein in the regulation of dopamine biosynthesis, J. Neurosci. 22 (2002) 3090-3099]. We recently began exploring the impact of alpha-Syn on TH in vivo, by transducing dopaminergic neurons in alpha-Syn knockout mouse (ASKO) olfactory bulb using wild type human alpha-Syn lentivirus. At 3.5-21 days after viral delivery, alpha-Syn expression was transduced primarily in periglomerular dopaminergic neurons. Cells with modest levels of alpha-Syn consistently co-labeled for Total-TH. However, cells bearing aggregated alpha-Syn, as revealed by proteinase K or Thioflavin-S treatment had significantly reduced Total-TH immunoreactivity, but high phosphoserine-TH labeling. On immunoblots, we noted that Total-TH immunoreactivity was equivalent in all conditions, although tissues with alpha-Syn aggregates again had higher phosphoserine-TH levels. This suggests that aggregated alpha-Syn is no longer able to inhibit TH. Although the reason(s) underlying reduced Total-TH immunoreactivity on tissue sections await(s) confirmation, the dopaminergic phenotype was easily verified using phosphorylation-state-specific TH antibodies. These findings have implications not only for normal alpha-Syn function in TH regulation, but also for measuring cell loss that is associated with synucleinopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–52. - PubMed
-
- Alves da Costa C, Paitel E, Vincent B, Checler F. Alpha-synuclein lowers p53-dependent apoptotic response of neuronal cells. Abolishment by 6-hydroxydopamine and implication for Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:50980–4. - PubMed
-
- Biere AL, Wood SJ, Wypych J, Steavenson S, Jiang Y, Anafi D, Jacobsen FW, Jarosinski MA, Wu GM, Louis JC, Martin F, Narhi LO, Citron M. Parkinson’s disease-associated alpha-synuclein is more fibrillogenic than beta- and gamma-synuclein and cannot cross-seed its homologs. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34574–9. - PubMed
-
- Bobrovskaya L, Dunkley PR, Dicksosteron PW. Phosphorylation of Ser19 increases both Ser40 phosphorylation and enzyme activity of tyrosine hydroxylase in intact cells. J Neurochem. 2004;90:857–64. - PubMed
-
- Campbell DG, Hardie DG, Vulliet PR. Identification of four phosphorylation sites in the N-terminal region of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:10489–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

