How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
- PMID: 18314333
- PMCID: PMC3242477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.01.007
How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
Abstract
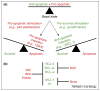
The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis proceeds when molecules sequestered between the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes are released to the cytosol by mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). This process is controlled by the BCL-2 family, which is composed of both pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins. Although there is no disagreement that BCL-2 proteins regulate apoptosis, the mechanism leading to MOMP remains controversial. Current debate focuses on what interactions within the family are crucial to initiate MOMP. Specifically, do the BH3-only proteins directly engage BAX and/or BAK activation or do these proteins solely promote apoptosis by neutralization of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins? We describe these models and contend that BH3-only proteins must perform both functions to efficiently engage MOMP and apoptosis.
Figures


References
-
- Chipuk JE, et al. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:1396–1402. - PubMed
-
- Riedl SJ, Salvesen GS. The apoptosome: signalling platform of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Newmeyer DD, et al. Cell-free apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts: inhibition by Bcl-2 and requirement for an organelle fraction enriched in mitochondria. Cell. 1994;79:353–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

