Islet amyloid in type 2 diabetes, and the toxic oligomer hypothesis
- PMID: 18314421
- PMCID: PMC2528855
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2007-0037
Islet amyloid in type 2 diabetes, and the toxic oligomer hypothesis
Abstract
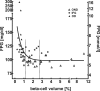
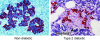
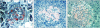
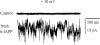
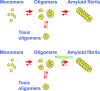
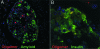
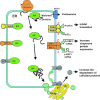
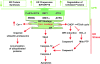
Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is characterized by insulin resistance, defective insulin secretion, loss of beta-cell mass with increased beta-cell apoptosis and islet amyloid. The islet amyloid is derived from islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP, amylin), a protein coexpressed and cosecreted with insulin by pancreatic beta-cells. In common with other amyloidogenic proteins, IAPP has the propensity to form membrane permeant toxic oligomers. Accumulating evidence suggests that these toxic oligomers, rather than the extracellular amyloid form of these proteins, are responsible for loss of neurons in neurodegenerative diseases. In this review we discuss emerging evidence to suggest that formation of intracellular IAPP oligomers may contribute to beta-cell loss in T2DM. The accumulated evidence permits the amyloid hypothesis originally developed for neurodegenerative diseases to be reformulated as the toxic oligomer hypothesis. However, as in neurodegenerative diseases, it remains unclear exactly why amyloidogenic proteins form oligomers in vivo, what their exact structure is, and to what extent these oligomers play a primary or secondary role in the cytotoxicity in what are now often called unfolded protein diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J 2001 Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787 - PubMed
-
- Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM, Frayling TM, Elliott KS, Lango H, Timpson NJ, Perry JR, Rayner NW, Freathy RM, Barrett JC, Shields B, Morris AP, Ellard S, Groves CJ, Harries LW, Marchini JL, Owen KR, Knight B, Cardon LR, Walker M, Hitman GA, Morris AD, Doney AS, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT 2007 Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316:1336–1341 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, Dina C, Shen L, Serre D, Boutin P, Vincent D, Belisle A, Hadjadj S, Balkau B, Heude B, Charpentier G, Hudson TJ, Montpetit A, Pshezhetsky AV, Prentki M, Posner BI, Balding DJ, Meyre D, Polychronakos C, Froguel P 2007 A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 445:881–885 - PubMed
-
- Jack Jr L, Boseman L, Vinicor F 2004 Aging Americans and diabetes. A public health and clinical response. Geriatrics 59:14–17 - PubMed
-
- Polonsky KS 2000 Dynamics of insulin secretion in obesity and diabetes. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(Suppl 2):S29–S31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

