Effect of interleukin-8 gene silencing with liposome-encapsulated small interfering RNA on ovarian cancer cell growth
- PMID: 18314475
- PMCID: PMC2770251
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djn024
Effect of interleukin-8 gene silencing with liposome-encapsulated small interfering RNA on ovarian cancer cell growth
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a proangiogenic cytokine that is overexpressed in many human cancers. We investigated the clinical and biologic significance of IL-8 in ovarian carcinoma using human samples and orthotopic mouse models.
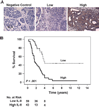
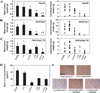
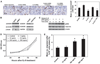
Methods: Tumor expression of IL-8 was assessed by immunohistochemistry among ovarian cancer patients (n = 102) with available clinical and survival data. We examined the effect of IL-8 gene silencing with small interfering RNAs incorporated into neutral liposomes (siRNA-DOPCs), alone and in combination with docetaxel, on in vivo tumor growth, angiogenesis (microvessel density), and tumor cell proliferation in mice (n = 10 per treatment group) bearing orthotopic taxane-sensitive (HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1) and taxane-resistant (SKOV3ip2.TR) ovarian tumors. All statistical tests were two-sided.
Results: Of the 102 cancer specimens, 43 (42%) had high IL-8 expression and 59 (58%) had low or no IL-8 expression; high IL-8 expression was associated with advanced tumor stage (P = .019), high tumor grade (P = .031), and worse survival (median survival for patients with high vs low IL-8 expression: 1.62 vs 3.79 years; P < .001). Compared with empty liposomes, IL-8 siRNA-DOPC reduced the mean tumor weight by 32% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 14% to 50%; P = .03) and 52% (95% CI = 27% to 78%; P = .03) in the HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1 mouse models, respectively. In all three mouse models, treatment with IL-8 siRNA-DOPC plus the taxane docetaxel reduced tumor growth the most compared with empty liposomes (77% to 98% reduction in tumor growth; P < .01 for all). In the HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1 models, tumors from mice treated with IL-8 siRNA-DOPC alone had lower microvessel density than tumors from mice treated with empty liposomes (HeyA8: 34% lower, 95% CI = 32% to 36% lower [P = .002]; SKOV3ip1: 39% lower, 95% CI = 34% to 44% lower [P = .007]). Compared with empty liposomes, IL-8 siRNA-DOPC plus docetaxel reduced tumor cell proliferation by 35% (95% CI = 25% to 44%; P < .001) and 38% (95% CI = 28% to 48%; P < .001) in the HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1 models, respectively.
Conclusions: Increased IL-8 expression is associated with poor clinical outcome in human ovarian carcinoma, and IL-8 gene silencing decreases tumor growth through antiangiogenic mechanisms.
Figures
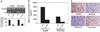
Similar articles
-
Silencing of p130cas in ovarian carcinoma: a novel mechanism for tumor cell death.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Nov 2;103(21):1596-612. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr372. Epub 2011 Sep 28. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21957230 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase targeting using in vivo short interfering RNA delivery in neutral liposomes for ovarian carcinoma therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Aug 15;12(16):4916-24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0021. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16914580 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and antivascular effects of EphA2 reduction with an agonistic antibody in ovarian cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Nov 1;98(21):1558-70. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj414. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006. PMID: 17077358
-
Functional roles of Src and Fgr in ovarian carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 1;17(7):1713-21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2081. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21300758 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic EphA2 gene targeting in vivo using neutral liposomal small interfering RNA delivery.Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 1;65(15):6910-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0530. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16061675
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-based delivery of small interfering RNA: challenges for cancer therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3637-57. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S23696. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22915840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of the IL-8 pathway for immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Oct 2;16(10):2312-2317. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1696075. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. Retraction in: Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2052703. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2052703. PMID: 31860375 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Enhanced reduction in cell viability by hyperthermia induced by magnetic nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:373-80. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S14613. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 21499427 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-8 is associated with adhesion, migration and invasion in human gastric cancer SCG-7901 cells.Med Oncol. 2012 Mar;29(1):91-9. doi: 10.1007/s12032-010-9780-0. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21191670
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibition Induces IκB Kinase (IKK)-dependent Interleukin-8/CXCL8 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 24;292(12):5043-5054. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.771014. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28167529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2007. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; [Accessed January 3, 2008]. www.cancer.org.
-
- Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS. Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2006;3(1):24–40. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. The role of VEGF in the regulation of physiological and pathological angiogenesis. EXS. 2005;(94):209–231. - PubMed
-
- Cooper BC, Ritchie JM, Broghammer CL, et al. Preoperative serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels: significance in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(10):3193–3197. - PubMed
-
- Lee JC, Chow NH, Wang ST, Huang SM. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colorectal cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36(6):748–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

