Glutamate transporter EAAT2 expression is up-regulated in reactive astrocytes in human periventricular leukomalacia
- PMID: 18314905
- PMCID: PMC2911955
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.21667
Glutamate transporter EAAT2 expression is up-regulated in reactive astrocytes in human periventricular leukomalacia
Abstract
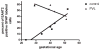
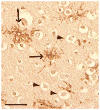
The major neuropathological correlate of cerebral palsy in premature infants is periventricular leukomalacia (PVL), a disorder of the immature cerebral white matter. Cerebral ischemia leading to excitotoxicity is thought to be important in the pathogenesis of this disorder, implying a critical role for glutamate transporters, the major determinants of extracellular glutamate concentration. Previously, we found that EAAT2 expression is limited primarily to premyelinating oligodendrocytes early in development and is rarely observed in astrocytes until >40 weeks. In this study, we analyzed the expression of EAAT2 in cerebral white matter from PVL and control cases. Western blot analysis suggested an up-regulation of EAAT2 in PVL compared with control cases. Single- and double-label immunocytochemistry showed a significantly higher percentage of EAAT2-immunopositive astrocytes in PVL (51.8% +/- 5.6%) compared with control white matter (21.4% +/- 5.6%; P = 0.004). Macrophages in the necrotic foci in PVL also expressed EAAT2. Premyelinating oligodendrocytes in both PVL and control cases expressed EAAT2, without qualitative difference in expression. The previously unrecognized up-regulation of EAAT2 in reactive astrocytes and its presence in macrophages in PVL reported here may reflect a response to either hypoxic-ischemic injury or inflammation.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

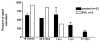





References
-
- Back SA, Craig A, Kayton RJ, Luo NL, Meshul CK, Allcock N, Fern R. Hypoxia-ischemia preferentially triggers glutamate depletion from oligodendroglia and axons in perinatal cerebral white matter. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:334–347. - PubMed
-
- Banker BQ, Larroche JC. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962;7:386–410. - PubMed
-
- Beschorner R, Dietz K, Schauer N, Mittelbronn M, Schluesener HJ, Trautmann K, Meyermann R, Simon P. Expression of EAAT1 reflects a possible neuroprotective function of reactive astrocytes and activated microglia following human traumatic brain injury. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22:515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

