The transferrin receptor modulates Hfe-dependent regulation of hepcidin expression
- PMID: 18316026
- PMCID: PMC2292811
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.016
The transferrin receptor modulates Hfe-dependent regulation of hepcidin expression
Abstract
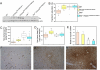
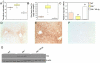
Hemochromatosis is caused by mutations in HFE, a protein that competes with transferrin (TF) for binding to transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1). We developed mutant mouse strains to gain insight into the role of the Hfe/Tfr1 complex in regulating iron homeostasis. We introduced mutations into a ubiquitously expressed Tfr1 transgene or the endogenous Tfr1 locus to promote or prevent the Hfe/Tfr1 interaction. Under conditions favoring a constitutive Hfe/Tfr1 interaction, mice developed iron overload attributable to inappropriately low expression of the hormone hepcidin. In contrast, mice carrying a mutation that interferes with the Hfe/Tfr1 interaction developed iron deficiency associated with inappropriately high hepcidin expression. High-level expression of a liver-specific Hfe transgene in Hfe-/- mice was also associated with increased hepcidin production and iron deficiency. Together, these models suggest that Hfe induces hepcidin expression when it is not in complex with Tfr1.
Figures



References
-
- Aisen P, Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annual Reviews of Biochemistry. 1980;49:357–393. - PubMed
-
- Ajioka RS, Levy JE, Andrews NC, Kushner JP. Regulation of iron absorption in Hfe mutant mice. Blood. 2002;100:1465–1469. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MJ, Lebron JA, Bjorkman PJ. Crystal structure of the hereditary haemochromatosis protein HFE complexed with transferrin receptor. Nature. 2000;403:46–53. - PubMed
-
- Beutler E, Gelbart T, Lee P, Trevino R, Fernandez MA, Fairbanks VF. Molecular characterization of a case of atransferrinemia. Blood. 2000;96:4071–4074. - PubMed
-
- Bralet MP, Duclos-Vallee JC, Castaing D, Samuel D, Guettier C. No hepatic iron overload 12 years after liver transplantation for hereditary hemochromatosis. Hepatology. 2004;40:762. author reply 762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

