Migratory neighbors and distant invaders: tumor-associated niche cells
- PMID: 18316475
- PMCID: PMC2731657
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1636908
Migratory neighbors and distant invaders: tumor-associated niche cells
Abstract
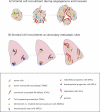
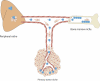
The cancer environment is comprised of tumor cells as well as a wide network of stromal and vascular cells participating in the cellular and molecular events necessary for invasion and metastasis. Tumor secretory factors can activate the migration of host cells, both near to and far from the primary tumor site, as well as promote the exodus of cells to distant tissues. Thus, the migration of stromal cells and tumor cells among specialized microenvironments takes place throughout tumor and metastatic progression, providing evidence for the systemic nature of a malignancy. Investigations of the tumor-stromal and stromal-stromal cross-talk involved in cellular migration in cancer may lead to the design of novel therapeutic strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Ara T., Tokoyoda K., Sugiyama T., Egawa T., Kawabata K., Nagasawa T. Long-term hematopoietic stem cells require stromal cell-derived factor-1 for colonizing bone marrow during ontogeny. Immunity. 2003;19:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Arafat W.O., Casado E., Wang M., Alvarez R.D., Siegal G.P., Glorioso J.C., Curiel D.T., Gomez-Navarro J. Genetically modified CD34+ cells exert a cytotoxic bystander effect on human endothelial and cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000;6:4442–4448. - PubMed
-
- Asou Y., Rittling S.R., Yoshitake H., Tsuji K., Shinomiya K., Nifuji A., Denhardt D.T., Noda M. Osteopontin facilitates angiogenesis, accumulation of osteoclasts, and resorption in ectopic bone. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1325–1332. - PubMed
-
- Atula S., Grenman R., Syrjanen S. Fibroblasts can modulate the phenotype of malignant epithelial cells in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 1997;235:180–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
