Single-dose safety and pharmacokinetics of ST-246, a novel orthopoxvirus egress inhibitor
- PMID: 18316519
- PMCID: PMC2346641
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01303-07
Single-dose safety and pharmacokinetics of ST-246, a novel orthopoxvirus egress inhibitor
Abstract
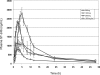
ST-246 is a novel, potent orthopoxvirus egress inhibitor that is being developed to treat pathogenic orthopoxvirus infections of humans. This phase I, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled single ascending dose study (first time with humans) was conducted to determine the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of ST-246 in healthy human volunteers. ST-246 was administered in single oral doses of 500, 1,000, and 2,000 mg to fasting healthy volunteers and 1,000 mg to nonfasting healthy volunteers. ST-246 was generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events, and no subject was withdrawn from the study due to ST-246. The most commonly reported drug-related adverse event was neutropenia, which was found, upon further analysis, not to be treatment related. ST-246 was readily absorbed following oral administration with mean times to maximum concentration from 2 h to 3 h. Absorption was greater in nonfasting volunteers than in fasting volunteers. Administration of ST-246 resulted in exposure levels predicted to be sufficient for inhibiting orthopoxvirus replication compared to exposure levels in nonhuman primates in which ST-246 protected animals from lethal orthopoxvirus infection.
Figures

References
-
- Bailey, T. R., S. R. Rippin, E. Opsitnick, C. J. Burns, D. C. Pevear, M. S. Collett, G. Rhodes, S. Tohan, J. W. Huggins, R. O. Baker, E. R. Kern, K. A. Keith, D. Dai, G. Yang, D. Hruby, and R. Jordan. 2007. N-(3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop[f]isoindol-2-(1H)-yl)carboxamides: identification of novel orthopoxvirus egress inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 50:1442-1444. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray, M. 2003. Pathogenesis and potential antiviral therapy of complications of smallpox vaccination. Antivir. Res. 58:101-114. - PubMed
-
- Charman, W. N., C. J. Porter, S. Mithani, and J. B. Dressman. 1997. Physiochemical and physiological mechanisms for the effects of food on drug absorption: the role of lipids and pH. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:269-282. - PubMed
-
- Division of AIDS, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health. 2004. Division of AIDS table for grading the severity of adult and pediatric adverse events. http://www3.niaid.nih.gov/research/resources/DAIDSClinRsrch/PDF/Safety/D....
-
- Fenner, F., D. A. Henderson, I. Arita, Z. Jazek, and I. D. Ladnyi. 1988. Smallpox and its eradication. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

