High Mobility Group Box Protein-1 correlates with renal function in chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- PMID: 18317568
- PMCID: PMC2258159
- DOI: 10.2119/2007-00107.Bruchfeld
High Mobility Group Box Protein-1 correlates with renal function in chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Abstract
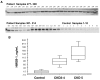
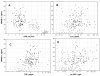
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with inflammation and malnutrition and carries a markedly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). High Mobility Group Box Protein-1 (HMGB-1) is a 30-kDa nuclear and cytosolic protein known as a transcription and growth factor, recently identified as a proinflammatory mediator of tissue injury. Recent data implicates HMGB-1 in endotoxin lethality, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis. The aim of this post-hoc, cross-sectional study was to determine whether HMGB-1 serum levels are elevated in CKD patients. The study groups were categorized as follows: 110 patients starting dialysis defined as CKD 5; 67 patients with moderately to severely reduced renal function or CKD 3-4; and 48 healthy controls. High-sensitivity C-reactive-protein (hs-CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), serum-albumin (S-albumin), hemoglobin A(1c) (HbA(1c)), hemoglobin, subjective global nutritional assessment (SGA), and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) were analyzed. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare groups and Spearman's rank correlation test was used for continuous variables. HMGB-1, measured by Western blot, was significantly (P < 0.001) elevated in CKD 5 (146.7 +/- 58.6 ng/mL) and CKD 3-4 (85.6 +/- 31.8) compared with controls (10.9 +/- 10.5). HMGB-1 levels were correlated positively with TNF (Rho = 0.52; P < 0.001), hs-CRP (Rho = 0.38; P < 0.001), IL-6 (Rho = 0.30; P < 0.001), HbA(1c) (Rho = 0.14; P = 0.02) and SGA (Rho = 0.21; P = 0.002) and negatively correlated with GFR (Rho = -0.69; P = 0.0001), Hb (Rho = -0.60; P < 0.001), S-albumin (Rho = -0.31; P < 0.001). The current study has revealed that HMGB-1 is elevated significantly in CKD patients and correlates with GFR as well as markers of inflammation and malnutrition. Future studies may delineate whether HMGB-1 is also a marker of disease activity and severity as well as a predictor of outcome in CKD.
Figures
References
-
- Stenvinkel P, et al. IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-alpha: central factors in the altered cytokine network of uremia—the good, the bad, and the ugly. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1216–33. - PubMed
-
- Avesani CM, Carrero JJ, Axelsson J, Qureshi AR, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P. Inflammation and wasting in chronic kidney disease. Partners in crime Kidney Int. 2006;70:S8–13.
-
- Panichi V, et al. Interleukin-6 is a stronger predictor of total and cardiovascular mortality than C-reactive protein in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:1154–60. - PubMed
-
- Honda H, et al. Serum albumin, C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and fetuin a as predictors of malnutrition, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in patients with ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:139–48. - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:S112–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

