Late results of absorbable pin fixation in the treatment of radial head fractures
- PMID: 18317861
- PMCID: PMC2311474
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0134-6
Late results of absorbable pin fixation in the treatment of radial head fractures
Abstract
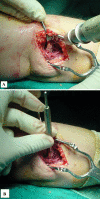
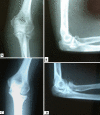
The use of bioabsorbable pins with prolonged degradation periods for fracture fixation has raised concerns about adverse soft tissue reactions, including seromas, discharging sinuses, or osteolytic changes. We asked whether bioabsorbable pins of self-reinforced polylactic acid polymer used in radial head fractures resulted in such reactions. We retrospectively reviewed 21 patients followed a minimum of 36 months (mean, 81 months; range, 36-136 months). There were nine Mason II, 10 Mason III, and two Mason IV fractures, which were evaluated clinically and radiographically. All fractures healed well with no radiographic signs of osteolysis. The mean Mayo Elbow Performance score was 93.8 (range, 20-100), which is comparable to the outcome of historical groups with radial head arthroplasty. The mean range of flexion of the elbow was 9 degrees to 132 degrees , with 79 degrees pronation and 77 degrees supination. The grip strength of the operated arm was not affected in comparison to the contralateral arm (mean range, 38.6 versus 40.9 kg). No material-related adverse effects were observed during and beyond the degradation period. Our data suggest concerns about soft tissue or bony reactions from these materials in radial head fractures are not justified.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2106/JBJS.E.01052', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.e.01052'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16951104', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16951104/'}]}
- Akesson T, Herbertsson P, Josefsson PO, Hasserius R, Besjakov J, Karlsson MK. Primary nonoperative treatment of moderately displaced two-part fractures of the radial head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1909–1914. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14960671', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14960671/'}]}
- Ashwood N, Bain GI, Unni R. Management of Mason type-III radial head fractures with a titanium prosthesis, ligament repair, and early mobilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:274–280. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00129-0', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00129-0'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11071611', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11071611/'}]}
- Böstman O, Pihlajamäki H. Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal fixation: a review. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2615–2621. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00003086-200002000-00026', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200002000-00026'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10693569', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10693569/'}]}
- Böstman OM, Pihlajamäki HK. Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable fixation devices. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:216–227. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3722222', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3722222/'}]}
- Broberg MA, Morrey BF. Results of delayed excision of the radial head after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:669–674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

