Triptans in the Italian population: a drug utilization study and a literature review
- PMID: 18317865
- PMCID: PMC3476185
- DOI: 10.1007/s10194-008-0020-3
Triptans in the Italian population: a drug utilization study and a literature review
Abstract
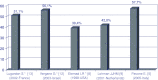
Previous studies performed in selected populations show a poor utilization of triptans for migraine. The objectives of our study were to establish patterns of triptans utilization in a large sample, covering 1/10 of Italian population (5.57 millions), and to perform a review of published studies on this topic. We investigated drug prescription database collected during 2006 from 33 health authorities distributed in 8 different regions. About 0.6% of the subjects received at least one prescription of triptans in 1 year: 77.7% were females and 22.3% males. Age distribution shows that 9.5% of patients were aged above 65, and received prescriptions for 8.2% of packages. The review of the literature suggests that these percentages of utilization are common to several countries, and shows that occasional triptan users who received only one prescription in 1 year are a large percentage (40-60%); moreover, a minor population of triptan users utilize a large amount of total triptans. Finally triptans are frequently prescribed in people aged above 65 years, a population in which triptans are contraindicated or not recommended. Our study and the analyzed ones indicate suboptimal treatment of migraine patients with triptans and also an incorrect use in some patients (triptan abusers, elderly).
Figures
References
-
- Panconesi A, Pavone E, Banfi R. Triptan utilization patterns: a study based on patients prescription records of an Italian health authority in Tuscany. J Headache Pain. 2006;7:266–267.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical