Integration of gene dosage and gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer, identification of HSP90 as potential target
- PMID: 18320023
- PMCID: PMC2254495
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001722
Integration of gene dosage and gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer, identification of HSP90 as potential target
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer causes approximately 1.2 million deaths per year worldwide, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents 85% of all lung cancers. Understanding the molecular events in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is essential to improve early diagnosis and treatment for this disease.
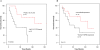
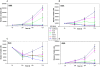
Methodology and principal findings: In an attempt to identify novel NSCLC related genes, we performed a genome-wide screening of chromosomal copy number changes affecting gene expression using microarray based comparative genomic hybridization and gene expression arrays on 32 radically resected tumor samples from stage I and II NSCLC patients. An integrative analysis tool was applied to determine whether chromosomal copy number affects gene expression. We identified a deletion on 14q32.2-33 as a common alteration in NSCLC (44%), which significantly influenced gene expression for HSP90, residing on 14q32. This deletion was correlated with better overall survival (P = 0.008), survival was also longer in patients whose tumors had low expression levels of HSP90. We extended the analysis to three independent validation sets of NSCLC patients, and confirmed low HSP90 expression to be related with longer overall survival (P = 0.003, P = 0.07 and P = 0.04). Furthermore, in vitro treatment with an HSP90 inhibitor had potent antiproliferative activity in NSCLC cell lines.
Conclusions: We suggest that targeting HSP90 will have clinical impact for NSCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu JQ, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Sekido Y, Fong KM, Minna JD. Molecular genetics of lung cancer. Annual Review of Medicine-Selected Topics in the Clinical Sciences. 2003;54:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Balsara BR, Testa JR. Chromosomal imbalances in human lung cancer. Oncogene. 2002;21:6877–6883. - PubMed
-
- Chin K, DeVries S, Fridlyand J, Spellman PT, Roydasgupta R, et al. Genomic and transcriptional aberrations linked to breast cancer pathophysiologies. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:529–541. - PubMed
-
- van de Wiel MA, Kim KI, Vosse SJ, van Wieringen WN, Wilting SM, et al. CGHcall: calling aberrations for array CGH tumor profiles. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:892–894. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

