Signaling signatures and functional properties of anti-human CD28 superagonistic antibodies
- PMID: 18320029
- PMCID: PMC2246163
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001708
Signaling signatures and functional properties of anti-human CD28 superagonistic antibodies
Abstract
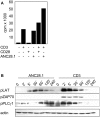
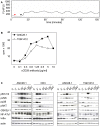
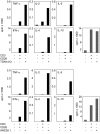
Superagonistic CD28 antibodies (CD28SAs) activate T lymphocytes without concomitant perturbation of the TCR/CD3-complex. In rodents these reagents induce the preferential expansion of regulatory T cells and can be used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Unexpectedly, the humanized CD28 superagonist TGN1412 caused severe and life threatening adverse effects during a recently conducted phase I clinical trail. The underlying molecular mechanisms are as yet unclear. We show that TGN1412 as well as the commercially available CD28 superagonist ANC28.1 induce a delayed but extremely sustained calcium response in human naïve and memory CD4+ T cells but not in cynomolgus T lymphocytes. The sustained Ca++-signal was associated with the activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways and together these events culminated in the rapid de novo synthesis of high amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, most notably IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. Importantly, sustained transmembranous calcium flux, activation of Src-kinases as well as activation of PI3K were found to be absolutely required for CD28SA-mediated production of IFN-gamma and IL-2. Collectively, our data suggest a molecular basis for the severe side effects caused by TGN1412 and impinge upon the relevance of non-human primates as preclinical models for reagents that are supposed to modify the function of human T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Schwartz RH. Costimulation of T lymphocytes: the role of CD28, CTLA-4, and B7/BB1 in interleukin-2 production and immunotherapy. Cell. 1992;71:1065–1068. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Abbas AK. T-cell costimulation–biology, therapeutic potential, and challenges. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:973–975. - PubMed
-
- Acuto O, Michel F. CD28-mediated co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:939–951. - PubMed
-
- Rudd CE, Schneider H. Unifying concepts in CD28, ICOS and CTLA4 co-receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:544–556. - PubMed
-
- Bischof A, Hara T, Lin CH, Beyers AD, Hunig T. Autonomous induction of proliferation, JNK and NF-alphaB activation in primary resting T cells by mobilized CD28. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:876–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

