CXCL5 promotes prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 18320069
- PMCID: PMC2262133
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.07976
CXCL5 promotes prostate cancer progression
Abstract
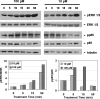
CXCL5 is a proangiogenic CXC-type chemokine that is an inflammatory mediator and a powerful attractant for granulocytic immune cells. Unlike many other chemokines, CXCL5 is secreted by both immune (neutrophil, monocyte, and macrophage) and nonimmune (epithelial, endothelial, and fibroblastic) cell types. The current study was intended to determine which of these cell types express CXCL5 in normal and malignant human prostatic tissues, whether expression levels correlated with malignancy and whether CXCL5 stimulated biologic effects consistent with a benign or malignant prostate epithelial phenotype. The results of these studies show that CXCL5 protein expression levels are concordant with prostate tumor progression, are highly associated with inflammatory infiltrate, and are frequently detected in the lumens of both benign and malignant prostate glands. Exogenous administration of CXCL5 stimulates cellular proliferation and gene transcription in both nontransformed and transformed prostate epithelial cells and induces highly aggressive prostate cancer cells to invade through synthetic basement membrane in vitro. These findings suggest that the inflammatory mediator, CXCL5, may play multiple roles in the etiology of both benign and malignant proliferative diseases in the prostate.
Figures






References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Koch AE. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: future targets? Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:710–721. - PubMed
-
- Begley L, Monteleon C, Shah RB, Macdonald JW, Macoska JA. CXCL12 overexpression and secretion by aging fibroblasts enhance human prostate epithelial proliferation in vitro. Aging Cell. 2005;4(6):291–298. - PubMed
-
- Begley LA, MacDonald JW, Day ML, Macoska JA. CXCL12 activates a robust transcriptional response in human prostate epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):26767–26774. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Singh UP, Grizzle WE, Lillard JW., Jr CXCL12-CXCR4 interactions modulate prostate cancer cell migration, metalloproteinase expression and invasion. Lab Invest. 2004;84(12):1666–1676. [PMID: 15467730] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
