Adjuvant high-dose interferon for cutaneous melanoma is most beneficial for patients with early stage III disease
- PMID: 18320602
- PMCID: PMC4207058
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23399
Adjuvant high-dose interferon for cutaneous melanoma is most beneficial for patients with early stage III disease
Abstract
Background: Evidence from randomized trials in the pre-sentinel lymph node biopsy era indicate that adjuvant treatment with high-dose interferon-alpha (IFN) increases recurrence-free survival (RFS) in patients with high-risk melanoma. However, to the authors' knowledge, the role of this treatment in selected patients with early stage III disease has not been well studied.
Methods: The clinical and pathologic characteristics of 486 patients undergoing surgical treatment for stage III melanoma were evaluated and the authors compared outcomes for those given adjuvant treatment with IFN with those patients who had surgery alone. A particular focus was on the effect of IFN therapy on RFS and overall survival (OS) among those patients with stage IIIA disease.
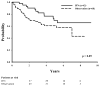
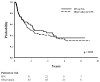
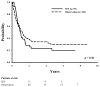
Results: The median follow-up for the entire cohort was 5.2 years; the 5-year RFS and OS rates for the entire group were 41% and 53%, respectively. Adjuvant IFN was given to 141 patients (29%). On multivariate analysis, IFN was found to be the only independent predictor for RFS in patients with stage IIIA disease (hazards ratio of 0.4; 95% confidence interval, 0.2-0.9 [P = .02]). IFN was not found to be associated with increased RFS in patients with more advanced lymph node disease (stage IIIB and stage IIIC). IFN appeared to have no effect on OS in any patient with stage III disease.
Conclusions: Adjuvant treatment with IFN improves RFS in melanoma patients with early stage III disease. The results of the current study should help guide management when considering adjuvant treatment for these patients.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, et al. An evidence-based staging system for cutaneous melanoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:131–149. - PubMed
-
- Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, et al. Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3635–3648. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Borden EC, Blum RH. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, et al. High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2444–2458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

