Role of videofluoroscopy in evaluation of neurologic dysphagia
- PMID: 18320837
- PMCID: PMC2640050
Role of videofluoroscopy in evaluation of neurologic dysphagia
Abstract
For many years, videofluoroscopy was considered the gold standard for studies on swallowing disorders, and only recently has its role been challenged, due primarily to the widespread use of videoendoscopy in the evaluation of dysphagia. Albeit, videofluoroscopy still maintains its key role in this area and, in particular, in studies on dysphagia of neurological origin, on account not only of the possibility, with this procedure, to achieve complete and dynamic evaluation of all phases of deglutition, but also the high sensitivity and specificity in revealing the presence of inhalation. Aim of the present investigation was to analyse the technical procedure of videofluoroscopy and the principal indications in the study of dysphagia of neurological origin, in the attempt to reveal the advantages and disadvantages occurring in this examination, also with respect to other methods adopted in the evaluation of dyphagia. In conclusion, at present, no instrumental examination can be defined as ideal for the study of swallowing, but it can be seen that, with each of these procedures, the information forthcoming is actually complementary, thus achieving the aim to proceed as correctly and rapidly as possible, with the management of patients with dysphagia.
La videofluoroscopia è stata considerata per anni il gold standard per lo studio delle alterazioni della deglutizione. Solo recentemente il suo ruolo è stato messo in discussione, principalmente a causa della diffusione che ha trovato la videoendoscopia nella valutazione della disfagia. La videofluoroscopia mantiene comunque il suo ruolo chiave in questo campo ed in particolare nello studio della disfagia di origine neurologica, grazie soprattutto alla possibilità che essa offre di valutare in modo completo e dinamico tutte le fasi della deglutizione e alla sua alta sensibilità e specificità nell’evidenziare la presenza di inalazione. In questo lavoro saranno analizzate le modalità di esecuzione della videofluoroscopia e le sue principali indicazioni nello studio della disfagia di origine neurologica, nel tentativo di evidenziare vantaggi e svantaggi presentati da questo esame, anche in rapporto alle altre metodiche utilizzate nella valutazione della disfagia. In conclusione attualmente nessun esame strumentale può essere definito come ideale per lo studio della deglutizione, ma esiste piuttosto una complementarietà tra le informazioni fornite da ciascuno, nell’obiettivo di ottenere una corretta e precoce presa in carico del paziente affetto da disfagia.
Figures
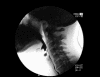
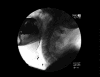
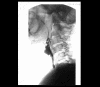
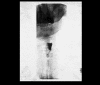
References
-
- Robbins J, Langmore S, Hind JA, Erlichman M. Dysphagia research in the 21st Century and beyond: proceedings from Dysphagia Experts Meeting, August 21, 2001. J Rehabil Res Dev 2002;39:543-8. - PubMed
-
- Donner MW, Siegel CI. The evaluation of pharyngeal neuromuscular disorders by cineradiography. Am J Roentgenol 1965;94:299-307.
-
- Logemann JA. Diagnosis and treatment of swallowing disorders. San Diego, California: College-Hill Press; 1983.
-
- Logemann JA. Manual for the videofluoroscopic study of swallowing. 2nd Edition. Austin, Texas: PRO-ED; 1993.
-
- Tesei F, Caliceti U, Farneti D, Brusori S, Gavelli GP, Mattioli S, et al. Lo studio endoscopico e per “imaging” della deglutizione. In: Piemonte M, editor. Fisiopatologia della deglutizione. Atti XIV Giornate Italiane di Otoneurologia. Milano: Formenti Ed.; 1997. p. 87.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
