Sensitization of pelvic afferent nerves in the in vitro rat urinary bladder-pelvic nerve preparation by purinergic agonists and cyclophosphamide pretreatment
- PMID: 18322018
- PMCID: PMC2891077
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00592.2007
Sensitization of pelvic afferent nerves in the in vitro rat urinary bladder-pelvic nerve preparation by purinergic agonists and cyclophosphamide pretreatment
Abstract
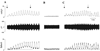
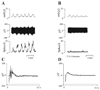
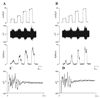
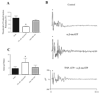
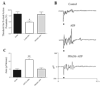
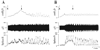
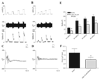
Effects of purinergic agonists (alpha,beta-meATP and ATP) and cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis on bladder afferent nerve (BAN) activity were studied in an in vitro bladder-pelvic nerve preparation. Distension of the bladder induced spontaneous bladder contractions that were accompanied by multiunit afferent firing. Intravesical administration of 40 and 130 microM alpha,beta-meATP increased afferent firing from 27 +/- 3 to 53 +/- 6 and 61 +/- 2 spikes/s, respectively, but did not change the maximum amplitude of spontaneous bladder contractions. Electrical stimulation on the surface of the bladder elicited action potentials (AP) in BAN. alpha,beta-meATP decreased the voltage threshold from 9.0 +/- 1.2 to 3.5 +/- 0.5 V (0.15-ms pulse duration) and increased the area of the APs (82% at 80-V stimulus intensity). These effects were blocked by TNP-ATP (30 microM). ATP (2 mM) applied in the bath produced similar changes in BAN activity. These effects were blocked by bath application of PPADS (30 microM). Neither TNP-ATP nor PPADS affected BAN activity induced by distension of the bladder. Cystitis induced by pretreatment of the rats with cyclophosphamide (100 mg/kg ip) increased afferent firing in response to isotonic bladder distension (10-40 cmH(2)O), decreased the threshold, and increased the area of evoked APs. The increase in afferent firing at 10 cmH(2)O intravesical pressure was reduced 52% by PPADS. These results indicate that purinergic agonists acting on P2X receptors and cystitis induced by cyclophosphamide can increase excitability of the BANs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide modulates bladder afferent nerve activity in the in vitro urinary bladder-pelvic nerve preparation from rats with cyclophosphamide induced cystitis.Brain Res. 2013 Jan 15;1490:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23063886 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of stimulation of muscarinic receptors on bladder afferent nerves in the in vitro bladder-pelvic afferent nerve preparation of the rat.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 18;1361:43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.018. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20840844 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nicotinic receptor agonists on bladder afferent nerve activity in an in vitro bladder-pelvic nerve preparation.Brain Res. 2016 Apr 15;1637:91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26876739 Free PMC article.
-
P2X3 knock-out mice reveal a major sensory role for urothelially released ATP.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 1;21(15):5670-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05670.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11466438 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk and sensitization of bladder afferent nerves.Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):77-81. doi: 10.1002/nau.20817. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010. PMID: 20025032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of urothelial or suburothelial cholinergic receptors on bladder reflexes in chronic spinal cord injured cats.Exp Neurol. 2016 Nov;285(Pt B):147-158. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27423814 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV4 blockade reduces voiding frequency, ATP release, and pelvic sensitivity in mice with chronic urothelial overexpression of NGF.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):F1695-F1706. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00147.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31630542 Free PMC article.
-
Role of detrusor PDGFRα+ cells in mouse model of cyclophosphamide-induced detrusor overactivity.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 24;12(1):5071. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09155-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35332235 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signalling underlies transforming growth factor-β-mediated bladder afferent nerve hyperexcitability.J Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;594(13):3575-88. doi: 10.1113/JP272148. Epub 2016 Apr 24. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27006168 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Transcutaneous Acupoint Electrical Stimulation on Urinary Retention and Urinary ATP in Elderly Patients After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial.Clin Interv Aging. 2022 Dec 1;17:1751-1760. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S382912. eCollection 2022. Clin Interv Aging. 2022. PMID: 36479561 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Birder LA, Barrick SR, Roppolo JR, Kanai AJ, de Groat WC, Kiss S, Buffington CA. Feline interstitial cystitis results in mechanical hypersensitivity and altered ATP release from bladder urothelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285:F423–F429. - PubMed
-
- Birder LA, Ruan HZ, Chopra B, Xiang Z, Barrick S, Buffington CA, Roppolo JR, Ford AP, de Groat WC, Burnstock G. Alterations in P2X and P2Y purinergic receptor expression in urinary bladder from normal cats and cats with interstitial cystitis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;287:F1084–F1091. - PubMed
-
- Borlak J, Zwadlo C. The myosin ATPase inhibitor 2,3-Butanedione monoxime dictates transcriptional activation of ion channels and Ca2+-handling proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:708–717. - PubMed
-
- Borvendeg-Khrasani M, Rubini P, Fischer W, Allgaier C, Wirkner K, Himmel HM, Gillen C, Illes P. Subsensitivity of P2X but not vanilloid 1 receptors in dorsal root ganglia of rats caused by cyclophosphamide cystitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;474:71–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

