Pax6 3' deletion results in aniridia, autism and mental retardation
- PMID: 18322702
- PMCID: PMC2719768
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-008-0484-x
Pax6 3' deletion results in aniridia, autism and mental retardation
Abstract
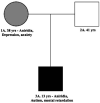
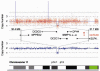
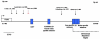
The PAX6 gene is a transcription factor expressed early in development, predominantly in the eye, brain and gut. It is well known that mutations in PAX6 may result in aniridia, Peter's anomaly and kertatisis. Here, we present mutation analysis of a patient with aniridia, autism and mental retardation. We identified and characterized a 1.3 Mb deletion that disrupts PAX6 transcriptional activity and deletes additional genes expressed in the brain. Our findings provide continued evidence for the role of PAX6 in neural phenotypes associated with aniridia.
Figures
References
-
- Azuma N, Yamada M. Missense mutation at the C terminus of the PAX6 gene in ocular anterior segment anomalies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:828–830. - PubMed
-
- Azuma N, Nishina S, Yanagisawa H, Okuyama T, Yamada M. PAX6 missense mutation in isolated foveal hypoplasia. Nat Genet. 1996;13:141–142. - PubMed
-
- Azuma N, Hotta Y, Tanaka H, Yamada M. Missense mutations in the PAX6 gene in aniridia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:2524–2528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

