Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in a large unselected general population in Japan
- PMID: 18322948
- PMCID: PMC2693682
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1358
Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in a large unselected general population in Japan
Abstract
Aim: To examine the prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms in a large unselected general population in Japan.
Methods: In Japan, mature adults are offered regular check-ups for the prevention of gastric cancer. A notice was sent by mail to all inhabitants aged>40 years. A total of 160983 Japanese (60774 male, 100209 female; mean age 61.9 years) who underwent a stomach check up were enrolled in this study. In addition, from these 160983 subjects, we randomly selected a total of 82894 (34275 male, 48619 female; mean age 62.4 years) to evaluate the prevalence of abdominal pain. The respective subjects were prospectively asked to complete questionnaires concerning the symptoms of heartburn, dysphagia, and abdominal pain for a 1 mo period.
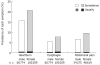
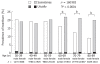
Results: The respective prevalences of the symptoms in males and females were: heartburn, 15.8% vs 20.7%; dysphagia, 5.4% vs 7.8%; and abdominal pain, 6.6% vs 9.6%. Among these symptoms, heartburn was significantly high compared with the other symptoms, and the prevalence of heartburn was significantly more frequent in females than in males in the 60-89-year age group. Dysphagia was also significantly more frequent in female patients.
Conclusion: The prevalence of typical GERD symptoms (heartburn) was high, at about 20% of the Japan population, and the frequency was especially high in females in the 60-89 year age group.
Figures
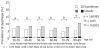
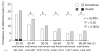
References
-
- Klauser AG, Schindlbeck NE, Muller-Lissner SA. Symptoms in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 1990;335:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Wong WM, Fass R. Extraesophageal and atypical manifestations of GERD. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19 Suppl 3:S33–S43. - PubMed
-
- Oda K, Iwakiri R, Hara M, Watanabe K, Danjo A, Shimoda R, Kikkawa A, Ootani A, Sakata H, Tsunada S, et al. Dysphagia associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease is improved by proton pump inhibitor. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:1921–1926. - PubMed
-
- Galmiche JP, Barthelemy P, Hamelin B. Treating the symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a double-blind comparison of omeprazole and cisapride. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;11:765–773. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

