Albumin therapy augments the effect of thrombolysis on local vascular dynamics in a rat model of arteriolar thrombosis: a two-photon laser-scanning microscopy study
- PMID: 18323493
- PMCID: PMC2699112
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502195
Albumin therapy augments the effect of thrombolysis on local vascular dynamics in a rat model of arteriolar thrombosis: a two-photon laser-scanning microscopy study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Results of our recent pilot clinical trial suggest that the efficacy of thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke may be enhanced by the coadministration of high-dose albumin. Here, we explored the microvascular hemodynamic effects of this combined therapy in a laboratory model of cortical arteriolar thrombosis.
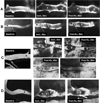
Methods: We studied the cortical microcirculation of physiologically monitored rats in vivo by two-photon laser-scanning microscopy after plasma-labeling with fluorescein-dextran. We induced focal thrombosis in 30- to 50-microm cortical arterioles by laser irradiation and measured arteriolar flow velocity by repeated line-scanning. At 30 minutes post-thrombosis, we treated animals with the thrombolytic agent, reteplase, which was coadministered with either human albumin, 2 g/kg, or with saline control.
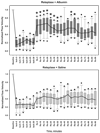
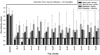
Results: Baseline arteriolar flow velocity averaged 3.8+/-0.7 mm/s, was immediately reduced by thrombosis to 22% to 25% of control values, and remained unchanged before treatment. Subthrombolytic doses of reteplase combined with saline led to a median increase in flow velocity to 37% of control distal to the thrombus (P=nonsignificant versus pretreatment). By contrast, reteplase combined with albumin therapy resulted in a prompt, highly significant increase of median flow velocity to 58% of control levels (P=0.013 versus reteplase+saline), which remained significantly higher than the reteplase+saline group at multiple time-points over the subsequent hour.
Conclusions: The beneficial effect of subthrombolytic doses of reteplase on microvascular hemodynamics distal to a cortical arteriolar thrombosis is markedly enhanced by the coadministration of high-dose albumin therapy; these results have important clinical implications for the management of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Albumin therapy improves local vascular dynamics in a rat model of primary microvascular thrombosis: a two-photon laser-scanning microscopy study.Stroke. 2008 Jan;39(1):198-204. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.495598. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Stroke. 2008. PMID: 18032741 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Modulation Augments Thrombolysis of Low-Dose Tissue Plasminogen Activator Following Cerebrovascular Thrombosis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 27;13:801727. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.801727. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720286 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin therapy of transient focal cerebral ischemia: in vivo analysis of dynamic microvascular responses.Stroke. 2002 Apr;33(4):1077-84. doi: 10.1161/hs0402.105555. Stroke. 2002. PMID: 11935064
-
Reteplase: a review of its use in the management of thrombotic occlusive disorders.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006;6(4):265-85. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200606040-00007. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16913828 Review.
-
Spotlight on reteplase in thrombotic occlusive disorders.BioDrugs. 2007;21(1):65-8. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721010-00008. BioDrugs. 2007. PMID: 17263591 Review.
Cited by
-
The Albumin in Acute Stroke Part 1 Trial: an exploratory efficacy analysis.Stroke. 2011 Jun;42(6):1621-5. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.610980. Epub 2011 May 5. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21546491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High-dose albumin treatment for acute ischaemic stroke (ALIAS) Part 2: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Neurol. 2013 Nov;12(11):1049-58. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70223-0. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Lancet Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24076337 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Malnutrition and Risk of Mortality in Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated With Intravenous Thrombolysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 21;14:834973. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.834973. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35264946 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional actions of approved and candidate stroke drugs.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Jan;6(1):43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2008.10.032. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19110198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Microvasculature in Cerebral Ischemia-Go (or Stop Going) with the Flow.Transl Stroke Res. 2011 Jun;2(2):136-7. doi: 10.1007/s12975-011-0076-2. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Transl Stroke Res. 2011. PMID: 24323619 No abstract available.
References
-
- Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Clemens JA, Ginsberg MD. Effect of delayed albumin hemodilution on infarction volume and brain edema after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Neurosurg. 1997;87:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Zhao W, Pattany PM, Weaver RG, Huh PW, Lin B, Busto R, Ginsberg MD. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging confirms marked neuroprotective efficacy of albumin therapy in focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1998;29:2587–2599. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Liu Y, Zhao W, Busto R, Ginsberg MD. Human albumin therapy of acute ischemic stroke: marked neuroprotective efficacy at moderate doses and with a broad therapeutic window. Stroke. 2001;32:553–560. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg MD, Hill MD, Palesch YY, Ryckborst KJ, Tamariz D. The ALIAS Pilot Trial: a dose-escalation and safety study of albumin therapy for acute ischemic stroke. I. Physiological responses and safety results. Stroke. 2006;37:2100–2106. - PubMed
-
- Palesch YY, Hill MD, Ryckborst KJ, Tamariz D, Ginsberg MD. The ALIAS Pilot Trial: a dose-escalation and safety study of albumin therapy for acute ischemic stroke. II. Neurological outcome and efficacy-analysis. Stroke. 2006;37:2107–2114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

