Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients
- PMID: 18323573
- PMCID: PMC2386905
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.P800003-JLR200
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients
Abstract
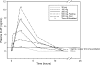
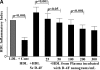
Patients with coronary heart disease or equivalent risk received a single dose of 30, 100, 300, or 500 mg of unformulated D-4F (n = 8, each dose) or placebo (n = 8) under fasting conditions. An additional 10 patients received 500 mg (n = 8) or placebo (n = 2) with a low-fat meal. There were no significant trends in any safety parameter. D-4F was detectable in plasma at all doses with a T(max) of 30 min, 1 h, and 2 h for 30, 100, and > or = 300 mg, respectively. The area under the curve((0-t)) was 27.81 ng/hr/ml and 54.71 ng/hr/ml for the 300 mg and 500 mg dose groups, respectively, and 17.96 ng/hr/ml for the 500 mg dose given with food. HDL from each time point for each subject was tested for its ability to inhibit LDL-induced monocyte chemotactic activity in cultures of human aortic endothelial cells. The values obtained were normalized to 1.0 for LDL alone to obtain the HDL inflammatory index. This index significantly improved at 4 h at the 300 mg dose and at 2 h at the 500 mg dose compared with placebo (P < 0.05). There were no changes in plasma lipid or lipoprotein levels. We conclude that unformulated D-4F has low bioavailability that is improved under fasting conditions, and that a single dose of D-4F is safe and well tolerated and may improve the HDL anti-inflammatory index.
Figures



References
-
- Kwiterovich P. O., Jr. 1998. The antiatherogenic role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am. J. Cardiol. 82 13Q–21Q. - PubMed
-
- Barter P. J., S. Nicholls, K. A. Rye, G. M. Anantharamaiah, M. Navab, and A. M. Fogelman. 2004. Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circ. Res. 95 764–772. - PubMed
-
- Moore R. E., M. A. Kawashiri, K. Kitajima, A. Secreto, J. S. Millar, D. Pratico, and D. J. Rader. 2003. Apolipoprotein A-I deficiency results in markedly increased atherosclerosis in mice lacking the LDL receptor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23 1914–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

