Direct linking of metabolism and gene expression in the proline utilization A protein from Escherichia coli
- PMID: 18324349
- PMCID: PMC2666929
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-008-0053-6
Direct linking of metabolism and gene expression in the proline utilization A protein from Escherichia coli
Abstract
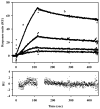
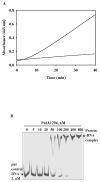
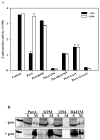
The control of gene expression by enzymes provides a direct pathway for cells to respond to fluctuations in metabolites and nutrients. One example is the proline utilization A (PutA) protein from Escherichia coli. PutA is a membrane-associated enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of L: -proline to glutamate using a flavin containing proline dehydrogenase domain and a NAD(+) dependent Delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase domain. In some Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli, PutA is also endowed with a ribbon-helix-helix DNA-binding domain and acts as a transcriptional repressor of the proline utilization genes. PutA switches between transcriptional repressor and enzymatic functions in response to proline availability. Molecular insights into the redox-based mechanism of PutA functional switching from recent studies are reviewed. In addition, new results from cell-based transcription assays are presented which correlate PutA membrane localization with put gene expression levels. General membrane localization of PutA, however, is not sufficient to activate the put genes.
Figures

References
-
- Abrahamson JLA, Baker LG, Stephenson JT, Wood JM. Proline dehydrogenase from Escherichia K12, properties of the membrane-associated enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1983;134:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Becker DF, Thomas EA. Redox properties of the PutA protein from Escherichia coli and the influence of the flavin redox state on PutA-DNA interactions. Biochemistry. 2001;40:4714–4722. - PubMed
-
- Brown E, Wood JM. Redesigned purification yields a fully functional PutA protein dimer from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13086–13092. - PubMed
-
- Brown ED, Wood JM. Conformational change and membrane association of the PutA protein are coincident with reduction of its FAD cofactor by proline. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:8972–8979. - PubMed
-
- Buckle M. Surface plasmon resonance applied to DNA-protein complexes. In: Moss T, editor. DNA-Protein Interactions: Principles and Protocols. Vol 148: Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana Press Inc.; Totowa, NJ: 2001. pp. 535–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

