The role of psychiatric disorders in the relationship between cigarette smoking and DSM-IV nicotine dependence among young adults
- PMID: 18324562
- PMCID: PMC2679531
- DOI: 10.1080/14622200801901898
The role of psychiatric disorders in the relationship between cigarette smoking and DSM-IV nicotine dependence among young adults
Abstract
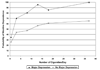
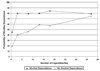
This study set out to evaluate the association between cigarette smoking and nicotine dependence (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders [4th ed.]) (DSM-IV), and to determine whether psychiatric disorders may signal greater sensitivity to nicotine dependence at similar levels of smoking exposure. Drawing on the young adult sample (aged 18-25 years) from the National Epidemiologic Survey of Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC), we conducted logistic regression analyses. Smokers with major depression, alcohol use disorders, or specific phobia had a higher risk of meeting DSM-IV criteria for nicotine dependence than did those without these disorders. When examining smoking quantity, we found that rates of nicotine dependence were similar for those with and without major depression among nondaily smokers, yet among daily smokers, rates of nicotine dependence were consistently higher among those with major depression than among those without. Alcohol dependence elevated the risk of nicotine dependence at low to moderate levels of use. However, no difference in risk for nicotine dependence was observed between alcohol-dependent and nondependent individuals smoking more than a pack a day. Increased risk of nicotine dependence among those with a specific phobia was consistent across the range of current smoking levels. These findings add to the growing literature documenting dependence in nondaily smokers and demonstrate that although chronic smoking is often a key feature in dependence, psychiatric disorders may signal greater sensitivity to nicotine dependence symptoms at substantially lower levels of smoking exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in the reporting of these findings.
Figures
References
-
- Bien TH, Burge R. Smoking and drinking: A review of the literature. International Journal of the Addictions. 1990;25:1429–1454. - PubMed
-
- Breslau N. Psychiatric comorbidity of smoking and nicotine dependence. Behavior Genetics. 1995;25:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Breslau N, Johnson EO, Hiripi E, Kessler R. Nicotine dependence in the United States: prevalence, trends, and smoking persistence. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2001;58:810–816. - PubMed
-
- Breslau N, Peterson EL, Schultz LR, Chilcoat HD, Andreski P. Major depression and stages of smoking: A longitudinal investigation. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1998;55:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Canino G, Bravo M, Ramirez R, Febo V, Fernandez R, Hasin D. The Spanish alcohol use disorder and associated disabilities interview schedule (AUDADIS): reliability and concordance with clinical diagnoses in a Hispanic population. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1999;60:790–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

