Dimensions of depressive symptoms and smoking cessation
- PMID: 18324570
- PMCID: PMC2650807
- DOI: 10.1080/14622200801901971
Dimensions of depressive symptoms and smoking cessation
Abstract
Because different psychopathologic components of depressive symptoms may have distinct etiologies, examining their differential effects on smoking cessation may elucidate mechanisms underlying the smoking-depression relationship. Negative affect (NA), somatic features (SF), low positive affect/anhedonia (PA), and interpersonal disturbance (IP) have been identified as unique dimensions of depression that can be measured using the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD). This study examined common and unique associations between CESD subscales and baseline smoking characteristics, nicotine withdrawal, and relapse in 157 participants enrolled in a smoking cessation trial for heavy social drinkers. Each dimension was univariately associated with negative and positive reinforcement smoking motives. Only SF had unique relations with tolerance smoking motives and univariate associations with nicotine dependence severity. Only PA predicted cessation-related changes in withdrawal symptoms on quit day. Analyses predicting abstinence at 8, 16, and 26 weeks post quit date showed that NA, SF, and PA each univariately predicted relapse, ps< or =.0083. Only low PA predicted poorer outcomes incrementally to the other dimensions, even when controlling for level of nicotine dependence, smoking frequency, and history of major depression, p = .0018. Interventions targeting anhedonia and low positive affect may be useful for smokers trying to quit.
Figures
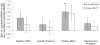
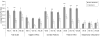
References
-
- al’Absi M, Hatsukami D, Davis GL. Attenuated adrenocorticotropic responses to psychological stress are associated with early smoking relapse. Psychopharmacology. 2005;181:107–117. - PubMed
-
- al’Absi M, Hatsukami D, Davis GL, Wittmers LE. Prospective examination of effects of smoking abstinence on cortisol and withdrawal symptoms as predictors of early smoking relapse. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2004;73:267–278. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Anda RF, Williamson DF, Escobedo LG, Mast EE, Giovino GA, Remington PL. Depression and the dynamics of smoking. A national perspective. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1990;264:1541–1545. - PubMed
-
- Beck A, Ward C, Mendelson M, Mack J, Erbaugh J. An inventory of measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1961;49:599–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

