Mycobacterium ulcerans disease, Peru
- PMID: 18325248
- PMCID: PMC2570831
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1403.070904
Mycobacterium ulcerans disease, Peru
Abstract
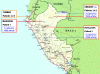
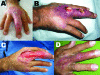
Eight adult patients (ages 18-58, 5 women) with Buruli ulcer (BU) confirmed by at least 2 diagnostic methods were seen in a 10-year period. Attempts to culture Mycobacterium ulcerans failed. Five patients came from jungle areas, and 3 from the swampy northern coast of Peru. The patients had 1-5 lesions, most of which were on the lower extremities. One patient had 5 clustered gluteal lesions; another patient had 2 lesions on a finger. Three patients were lost to follow-up. All 5 remaining patients had moderate disease. Diverse treatments (antituberculous drugs, World Health Organization [WHO] recommended antimicrobial drug treatment for BU, and for 3 patients, excision surgery) were successful. Only 1 patient (patient 7) received the specific drug treatment recommended by WHO. BU is endemic in Peru, although apparently infrequent. Education of populations and training of health workers are first needed to evaluate and understand the full extent of BU in Peru.
Figures
References
-
- Janssens PG, Pattyn SR, Meyers WM, Portaels F. Buruli ulcer: an historical overview with updating to 2005 [in French]. Bulletin des séances. Académie royale des Sciences d’outre-mer Bull. 2005;51:165–99.
-
- Portaels F, Meyers WM. Buruli ulcer. In: Faber WR, Hay RJ, Naafs B, editors. Imported skin diseases. Maarssen (the Netherlands): Elsevier Gezondheidszorg; 2006. pp. 117–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
