Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination
- PMID: 18326650
- PMCID: PMC2397368
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.120345
Three-dimensional resolution doubling in wide-field fluorescence microscopy by structured illumination
Abstract
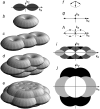
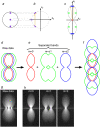
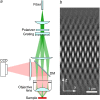
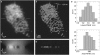
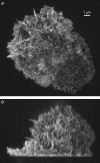
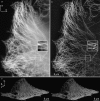
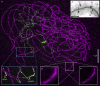
Structured illumination microscopy is a method that can increase the spatial resolution of wide-field fluorescence microscopy beyond its classical limit by using spatially structured illumination light. Here we describe how this method can be applied in three dimensions to double the axial as well as the lateral resolution, with true optical sectioning. A grating is used to generate three mutually coherent light beams, which interfere in the specimen to form an illumination pattern that varies both laterally and axially. The spatially structured excitation intensity causes normally unreachable high-resolution information to become encoded into the observed images through spatial frequency mixing. This new information is computationally extracted and used to generate a three-dimensional reconstruction with twice as high resolution, in all three dimensions, as is possible in a conventional wide-field microscope. The method has been demonstrated on both test objects and biological specimens, and has produced the first light microscopy images of the synaptonemal complex in which the lateral elements are clearly resolved.
Figures
References
-
- Agard, D. A., Y. Hiraoka, P. Shaw, and J. W. Sedat. 1989. Fluorescence microscopy in three dimensions. Methods Cell Biol. 30:353–377. - PubMed
-
- Pawley, J. B. 2006. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy. Plenum Press, New York.
-
- Diaspro, A. 2002. Confocal and Two-Photon Microscopy: Foundations, Applications, and Advances. Wiley-Liss, New York.
-
- Wilson, T. 1995. The role of the pinhole in confocal imaging system. In Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy. J. B. Pawley, editor. Plenum Press, New York.
-
- Gustafsson, M. G. L. 2000. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 198:82–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

