Construction of a functional CMP-sialic acid biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 18326787
- PMCID: PMC2330290
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.108.117572
Construction of a functional CMP-sialic acid biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis
Abstract
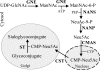
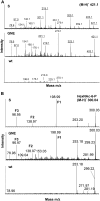
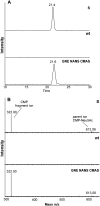
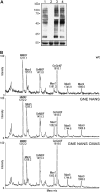
Previous studies have reported that plants contain negligible amounts of free or protein-bound N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac). This is a major disadvantage for the use of plants as a biopharmaceutical expression system, since N-glycans with terminal Neu5Ac residues are important for the biological activities and half-lives of recombinant therapeutic glycoproteins in humans. For the synthesis of Neu5Ac-containing N-glycans, plants have to acquire the ability to synthesize Neu5Ac and its nucleotide-activated derivative, cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid. In this study, we have generated transgenic Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) plants expressing three key enzymes of the mammalian Neu5Ac biosynthesis pathway: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase, N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphate synthase, and CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. Simultaneous expression of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase and N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphate synthase resulted in the generation of significant Neu5Ac amounts (1,275 nmol g(-1) fresh weight in leaves) in planta, which could be further converted to cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid (2.4 nmol g(-1) fresh weight in leaves) by coexpression of CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. These findings are a major step toward the production of Neu5Ac-containing glycoproteins in plants.
Figures




References
-
- Anumula KR (1994) Quantitative determination of monosaccharides in glycoproteins by high-performance liquid chromatography with highly sensitive fluorescence detection. Anal Biochem 220 275–283 - PubMed
-
- Cox KM, Sterling JD, Regan JT, Gasdaska JR, Frantz KK, Peele CG, Black A, Passmore D, Moldovan-Loomis C, Srinivasan M, et al (2006) Glycan optimization of a human monoclonal antibody in the aquatic plant Lemna minor. Nat Biotechnol 24 1591–1597 - PubMed
-
- Dirnberger D, Steinkellner H, Abdennebi L, Remy JJ, van de Wiel D (2001) Secretion of biologically active glycoforms of bovine follicle stimulating hormone in plants. Eur J Biochem 268 4570–4579 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

