Intracellular iron transport and storage: from molecular mechanisms to health implications
- PMID: 18327971
- PMCID: PMC2932529
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2007.1893
Intracellular iron transport and storage: from molecular mechanisms to health implications
Abstract
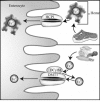
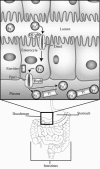
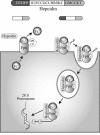
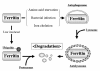
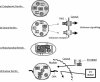
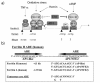
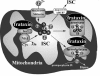
Maintenance of proper "labile iron" levels is a critical component in preserving homeostasis. Iron is a vital element that is a constituent of a number of important macromolecules, including those involved in energy production, respiration, DNA synthesis, and metabolism; however, excess "labile iron" is potentially detrimental to the cell or organism or both because of its propensity to participate in oxidation-reduction reactions that generate harmful free radicals. Because of this dual nature, elaborate systems tightly control the concentration of available iron. Perturbation of normal physiologic iron concentrations may be both a cause and a consequence of cellular damage and disease states. This review highlights the molecular mechanisms responsible for regulation of iron absorption, transport, and storage through the roles of key regulatory proteins, including ferroportin, hepcidin, ferritin, and frataxin. In addition, we present an overview of the relation between iron regulation and oxidative stress and we discuss the role of functional iron overload in the pathogenesis of hemochromatosis, neurodegeneration, and inflammation.
Figures






References
-
- Abboud S. Haile DJ. A novel mammalian iron-regulated protein involved in intracellular iron metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:19906–19912. - PubMed
-
- Adams PC. Powell LW. Halliday JW. Isolation of a human hepatic ferritin receptor. Hepatology. 1988;8:719–721. - PubMed
-
- Aisen P. Leibman A. Zweier J. Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:1930–1937. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mahdawi S. Pinto RM. Varshney D. Lawrence L. Lowrie MB. Hughes S. Webster Z. Blake J. Cooper JM. King R. Pook MA. GAA repeat expansion mutation mouse models of Friedreich ataxia exhibit oxidative stress leading to progressive neuronal and cardiac pathology. Genomics. 2006;88:580–590. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

