Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics by Arf-family GTPases
- PMID: 18328709
- PMCID: PMC2885709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.02.002
Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics by Arf-family GTPases
Abstract
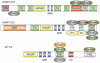
Small GTPases of the Arf family are best known for their role in vesicular transport, wherein they nucleate the assembly of coat proteins at sites of carrier vesicle formation. However, accumulating evidence indicates that the Arfs are also important regulators of actin cytoskeleton dynamics and are involved in a variety of actin-based processes, including cell adhesion, migration and neurite outgrowth. The mechanisms of this regulation are remarkably diverse, ranging from the integration of vesicular transport with cytoskeleton assembly to the direct regulation of Rho-family GTPase function. Here, we review recent progress in our understanding of how Arfs and their interacting proteins function to integrate membrane and cytoskeletal dynamics.
Figures


References
-
- Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005;21:247–269. - PubMed
-
- D’Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P. ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:347–358. - PubMed
-
- Yin HL, Janmey PA. Phosphoinositide regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003;65:761–789. - PubMed
-
- Godi A, et al. ARF mediates recruitment of PtdIns-4-OH kinase-beta and stimulates synthesis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 on the Golgi complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999;1:280–287. - PubMed
-
- Jones DH, et al. Type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase directly interacts with ADP-ribosylation factor 1 and is responsible for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis in the golgi compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:13962–13966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

